When you rely on headache meds too often, your body starts to fight back. This is called migraine overuse, a condition where frequent use of headache medications leads to more frequent and severe headaches. It’s not addiction—it’s physiology. Your brain gets used to the drug, and when it wears off, it triggers another attack. This cycle turns occasional migraines into daily pain. People often don’t realize they’re stuck in it because they think the medicine is helping, when really, it’s the main reason their headaches won’t go away.
rebound headaches, also known as medication overuse headache, occur when pain relievers or migraine-specific drugs are taken more than 10–15 days a month. Common culprits include over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, combination meds with caffeine or codeine, and prescription triptans like sumatriptan. Even if you’re only taking them on bad days, if those days add up, you’re at risk. Studies show that over 2% of the general population suffers from this, and it’s even higher among people with chronic migraines. The worst part? Stopping the meds feels awful at first—headaches get worse, nausea and anxiety spike. But that’s your brain resetting. Most people see real improvement after 2–8 weeks of quitting.
It’s not just about cutting back—it’s about replacing the habit. Many people jump from one drug to another, thinking a different pill will solve it. But the problem isn’t the drug—it’s the frequency. What works better is a plan: work with your doctor to taper off safely, use preventive treatments like beta-blockers or CGRP inhibitors if needed, and try non-drug strategies like sleep hygiene, stress management, or biofeedback. You don’t need to suffer through every headache. Sometimes, the most powerful tool is not taking anything at all.
Below, you’ll find real stories and science-backed advice from people who’ve been there. Some found relief by switching medications. Others broke the cycle with lifestyle changes. A few learned that their "migraines" were actually rebound headaches all along. These posts don’t offer quick fixes—they offer clarity. And sometimes, that’s the first step to feeling better.
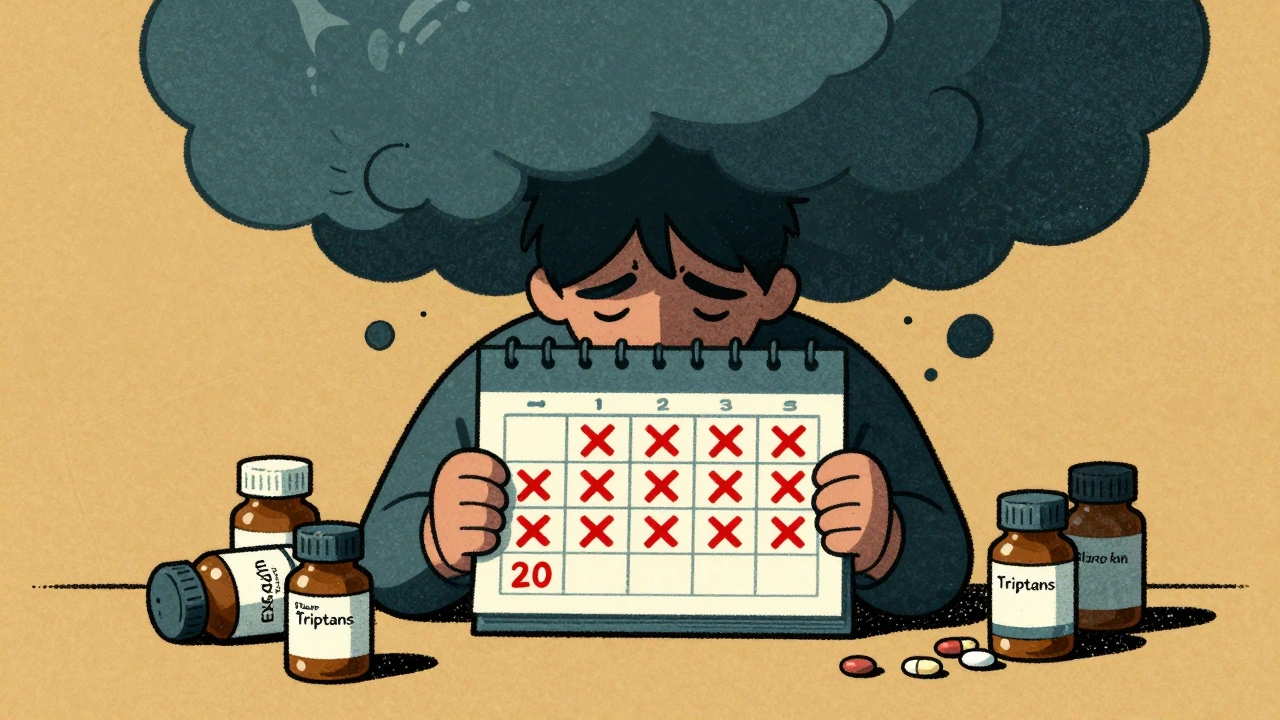

Medication overuse headaches are a hidden cause of chronic pain, triggered by too-frequent use of common painkillers. Learn how to identify them, safely stop the cycle, and find lasting relief with proven treatments.
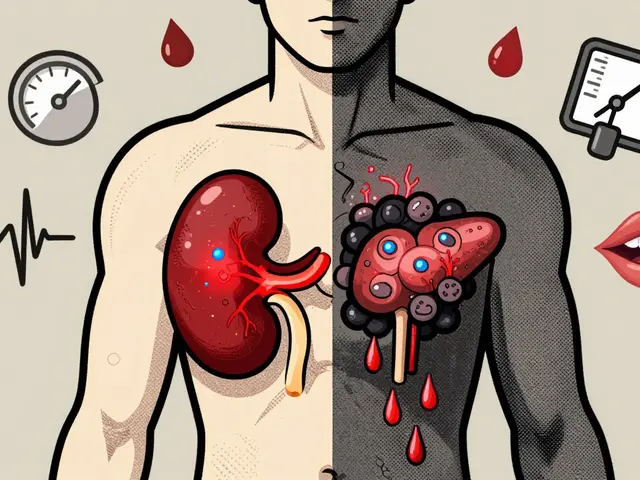
Cyclosporine and tacrolimus are essential for transplant patients but come with serious side effects like kidney damage, tremors, and diabetes. Learn how these drugs compare, what to watch for, and how doctors are now reducing their use to improve long-term health.

Governments don't set prices for generic drugs - they let competition do it. Learn how FDA approvals, FTC enforcement, and market forces keep generic medications affordable without direct price controls.
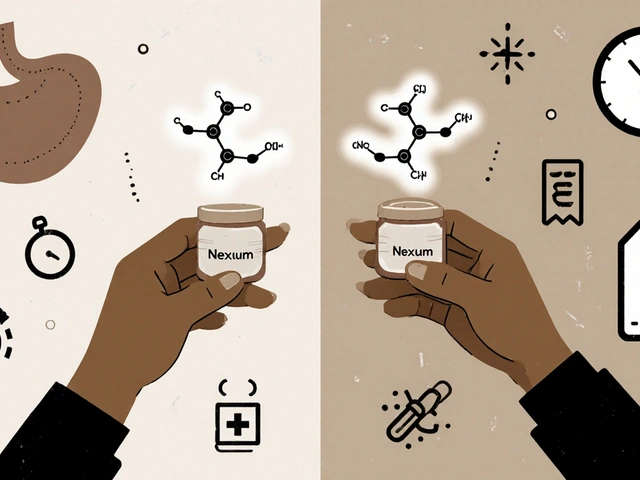
Compare Nexium (esomeprazole) with generic alternatives like omeprazole, lansoprazole, and pantoprazole. Learn which PPI works best for acid reflux, how to switch safely, and when lifestyle changes can replace medication.
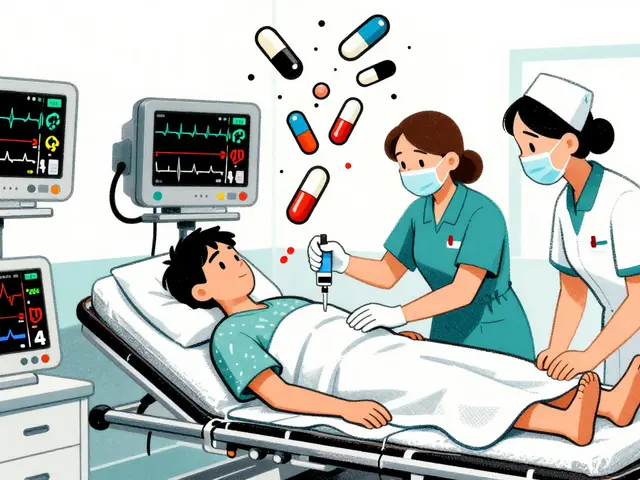
Multiple drug overdoses are deadly because substances interact unpredictably. Learn how naloxone, acetylcysteine, and emergency protocols work together to save lives when opioids, acetaminophen, or benzodiazepines are mixed.

Explore how support groups improve life for those with partial onset seizures, covering benefits, types, finding options, and tips for active participation.