When you're diagnosed with gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that affect how your body uses insulin. It's not your fault, and it doesn't mean you'll have diabetes forever—but what you eat matters a lot right now. About 1 in 10 pregnant women get it, and the good news is, most can manage it without insulin by adjusting their diet.
Your body is making more hormones during pregnancy, and those can block insulin from doing its job. That means sugar builds up in your blood, which can affect your baby’s growth and increase risks like preterm birth or a large baby. That’s why blood sugar control during pregnancy, keeping glucose levels within a safe range through food choices and timing is the main goal. It’s not about starving yourself or cutting out carbs entirely—it’s about choosing the right kinds, at the right times. low glycemic foods, carbs that break down slowly and don’t spike your blood sugar like oats, beans, lentils, non-starchy vegetables, and whole fruits are your friends. Pair them with protein and healthy fats to slow digestion even more. Avoid sugary drinks, white bread, pastries, and processed snacks—they’re quick energy bursts that leave you crashing and your blood sugar soaring.
Many women think they need to eat for two, but with gestational diabetes, it’s more about eating smart. Three small meals and two to three snacks a day help keep your levels steady. Breakfast is often the hardest—your body is most insulin resistant in the morning—so keep it light on carbs and heavy on protein and fiber. Think eggs with spinach and avocado instead of toast and jam. Snacks like Greek yogurt with berries, a handful of almonds, or hummus with cucumber slices work better than crackers or fruit juice. prenatal nutrition, the specific nutrient needs of pregnant women, especially those managing blood sugar still matters: you need folic acid, iron, calcium, and vitamin D just like any other pregnant person, but now you’re getting them from foods that won’t wreck your glucose levels.
Some women worry they’re being too strict, but this isn’t a diet you’re on for life—it’s a temporary adjustment to protect your baby and your own health. Once your baby is born, gestational diabetes usually goes away. But having it does raise your risk of type 2 diabetes later, so learning how to eat well now sets you up for long-term health. The changes you make today aren’t just about numbers on a glucose monitor—they’re about giving your baby the best start possible.
Below, you’ll find real, practical advice from women who’ve been there, plus clear guidance on what to eat, what to skip, and how to make meals that keep you full, satisfied, and in control—without feeling deprived.
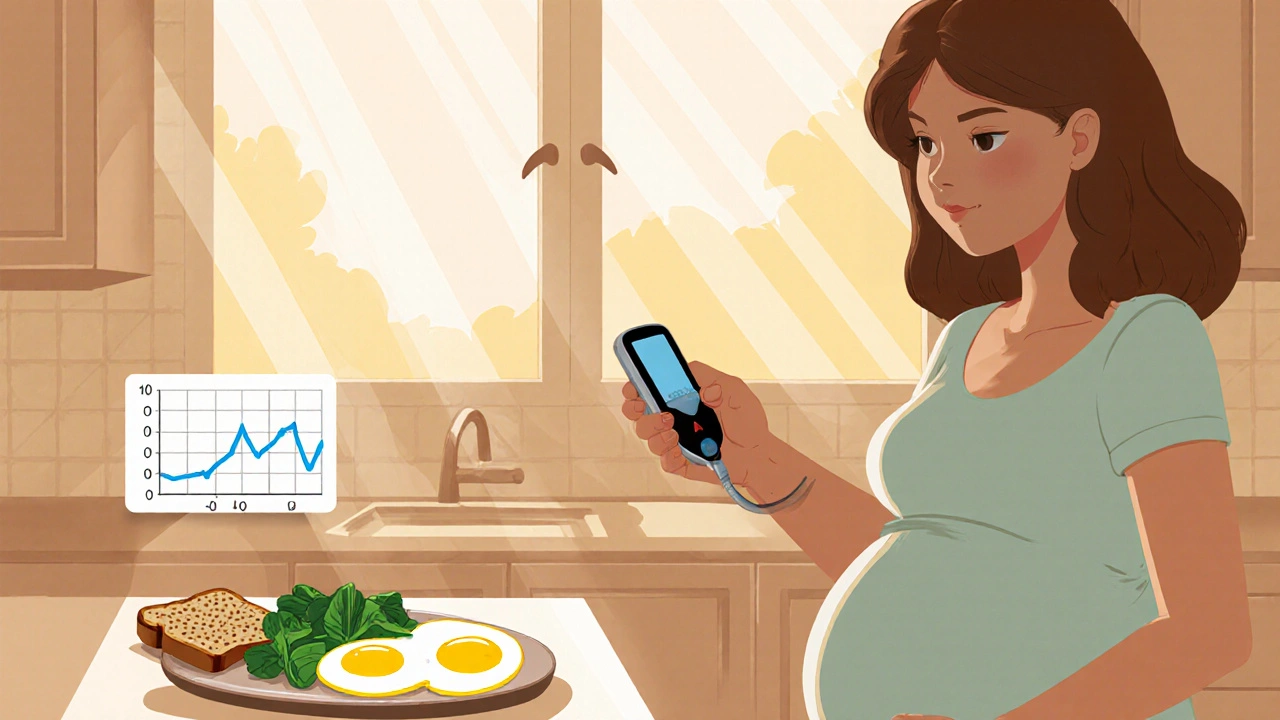
Learn how to manage gestational diabetes with diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring to reduce risks during pregnancy and protect long-term health for both mother and baby.

Over half of patients with chronic conditions skip or forget their medications due to cost, confusion, complex schedules, and fear of side effects. Understanding these barriers is the first step to better health outcomes.

This article dives into how online pharmacies handle privacy, secure packaging, and verification for erectile dysfunction medications. It covers the steps you can expect when ordering sensitive medications online and demystifies how discreet delivery works. You’ll get practical insights, tips, and real examples that help you shop for ED meds confidently. Whether you’re new to buying online or looking for safer ways to handle prescription privacy, this guide covers the details. Prepare to feel totally up-to-date on all things discreet in ED medication delivery.

Prior authorization is a common but confusing step in getting your prescription covered by insurance. Learn what drugs require it, how the process works, what to do if it's denied, and how to avoid delays.

SNRI medications offer a dual-action approach to treating depression and chronic pain by boosting serotonin and norepinephrine. Learn how they compare to SSRIs, their real-world effectiveness, side effects, and why they're a key option for treatment-resistant cases.
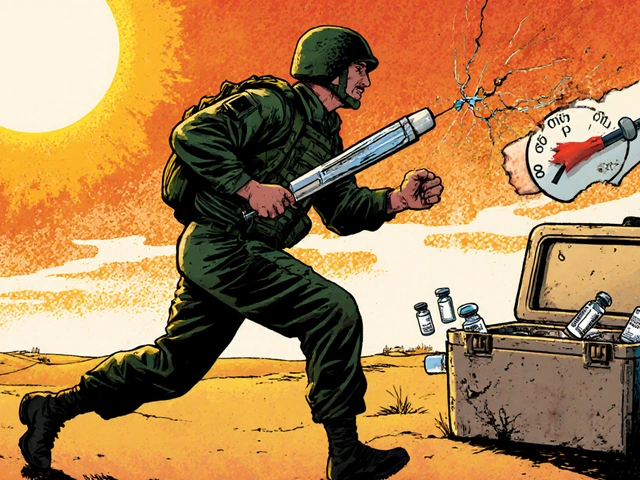
Military deployment exposes medications to extreme heat, storage failures, and access delays that can render life-saving drugs ineffective. From vaccines to insulin, improper storage threatens soldier readiness-and the military is racing to fix it.