When you pick up a generic pill at the pharmacy, you’re not just saving money—you’re participating in a system shaped by government generic drug policy, a set of rules and incentives designed to make essential medications affordable and widely available. Also known as public drug pricing strategy, this policy guides how generics enter the market, how insurers cover them, and who gets access. Without these rules, brand-name drugs would dominate shelves, and millions would skip doses because they can’t afford them.
The generic drugs, medications with the same active ingredients as brand-name drugs but sold at a fraction of the cost. Also known as generic medication, it are the backbone of this system. The FDA approves them after proving they work just like the original—same dose, same effect, same safety. But getting them to market isn’t just about science. It’s about law. The Hatch-Waxman Act of 1984 created the ANDA pathway, letting companies skip expensive clinical trials if they show bioequivalence. That’s why you can buy a $4 generic version of a $400 brand-name drug. But here’s the catch: how much you actually pay depends on your insurer’s formulary tiers, the ranked list of drugs your plan covers, with generics usually at the lowest cost tier. Also known as drug formulary, it. Some plans put certain generics in higher tiers if they’re newer or less commonly used. Others don’t cover them at all unless you try the brand first. And in Medicare Part D, your out-of-pocket costs can swing wildly based on where you are in the coverage gap.
State laws add another layer. Some states require pharmacists to substitute generics unless the doctor says no. Others let pharmacies choose which generic version to dispense based on cost. Meanwhile, the federal government pushes for more generics through bulk purchasing and rebate programs. But not all policies work the same. A drug covered under Medicaid might be denied under a private plan, even if it’s the exact same pill. That’s why switching health plans can mean big cost surprises—if you don’t check the formulary first.
What you’ll find in these posts isn’t theory. It’s real-world advice from people who’ve been burned by hidden costs, confused by tier changes, or shocked when their go-to generic vanished from their plan’s list. You’ll learn how to read your formulary, when to ask for a tier exception, how Medicare Part D changes every year, and which states have the strongest generic drug protections. You’ll also see how policies affect real drugs—from blood pressure meds like ramipril to antidepressants like amitriptyline—and how small changes in coverage can make a huge difference in your wallet and your health.

Governments don't set prices for generic drugs - they let competition do it. Learn how FDA approvals, FTC enforcement, and market forces keep generic medications affordable without direct price controls.

Trace the journey of HIV from its 1980s discovery to today’s advanced antiretroviral treatments, highlighting key milestones, scientists, and breakthroughs.

Prior authorization is a common but confusing step in getting your prescription covered by insurance. Learn what drugs require it, how the process works, what to do if it's denied, and how to avoid delays.
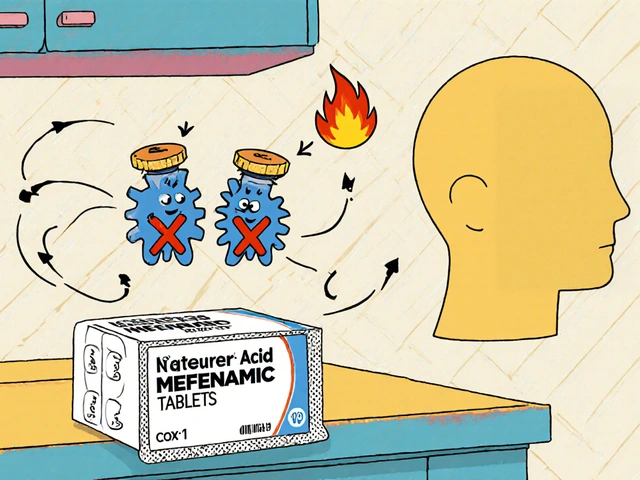
Explore how mefenamic acid influences bone mineral density, review clinical evidence, compare it with other NSAIDs, and get practical tips for patients and prescribers.

Detailed guidance on how to buy cimetidine online safely, including tips on reputable sources, avoiding scams, and key facts about this popular medication.
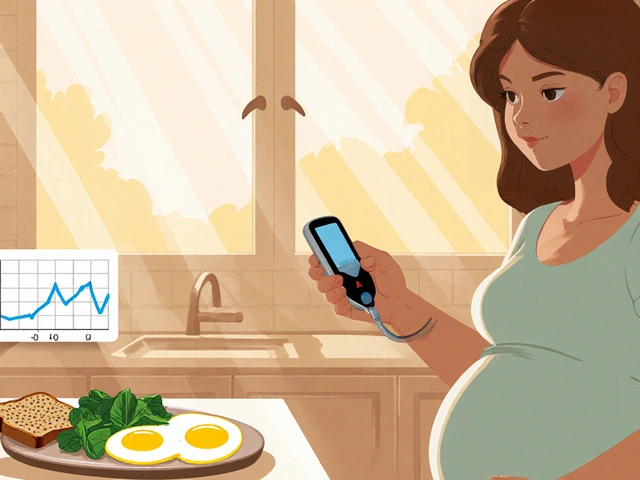
Learn how to manage gestational diabetes with diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring to reduce risks during pregnancy and protect long-term health for both mother and baby.