When your skin feels raw, tight, and itchy, eczema moisturizers, specialized creams and ointments designed to repair the skin barrier and lock in moisture for people with atopic dermatitis. Also known as emollients, they’re not just for comfort—they’re medical tools that stop the itch-scratch cycle before it worsens. Unlike regular lotions, these products are built to rebuild what eczema breaks down: the outer layer of your skin that keeps out irritants and holds in water.
Not all moisturizers are made equal. The best ones for eczema contain ceramides, fatty acids, and cholesterol—ingredients your skin naturally loses when flare-ups hit. Look for thick ointments like petroleum jelly or those labeled "fragrance-free" and "hypoallergenic." Avoid anything with alcohol, lanolin, or artificial scents—they might feel nice at first but can trigger more irritation down the line. A 2022 study in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology showed that people who used ceramide-rich moisturizers daily cut their flare-ups by nearly half compared to those who skipped them.
It’s not just about what you put on your skin—it’s about when and how. Apply moisturizer within three minutes after bathing, while your skin is still damp. This traps water in the top layer, making the barrier stronger over time. Use it at least twice a day, even when your skin looks fine. Skipping it during calm periods is like stopping your car’s oil change just because the engine isn’t smoking yet.
People with eczema often mix and match treatments—topical steroids, antihistamines, even light therapy—but moisturizers are the one thing every single expert agrees on. They’re the foundation. Without them, other treatments don’t work as well. Even if you’re using prescription creams, you still need a good moisturizer underneath to help them absorb properly and keep your skin from drying out again.
And don’t fall for the hype. Just because a product says "natural" or "organic" doesn’t mean it’s safe for eczema. Some plant oils, like coconut or tea tree, can irritate sensitive skin. Stick to simple formulas with fewer ingredients. If you’ve tried ten different creams and nothing sticks, start over with plain petroleum jelly—it’s cheap, effective, and has zero additives.
What you’ll find below are real-world reviews, comparisons, and tips from people who’ve lived with eczema for years. We’ve pulled together posts that break down what works, what doesn’t, and why some moisturizers cost five times more but do the same job as a dollar-store ointment. You’ll see how storage affects potency, why some products lose effectiveness in heat, and how to pick one that won’t sit unused on your shelf. No theory. No fluff. Just what actually helps.
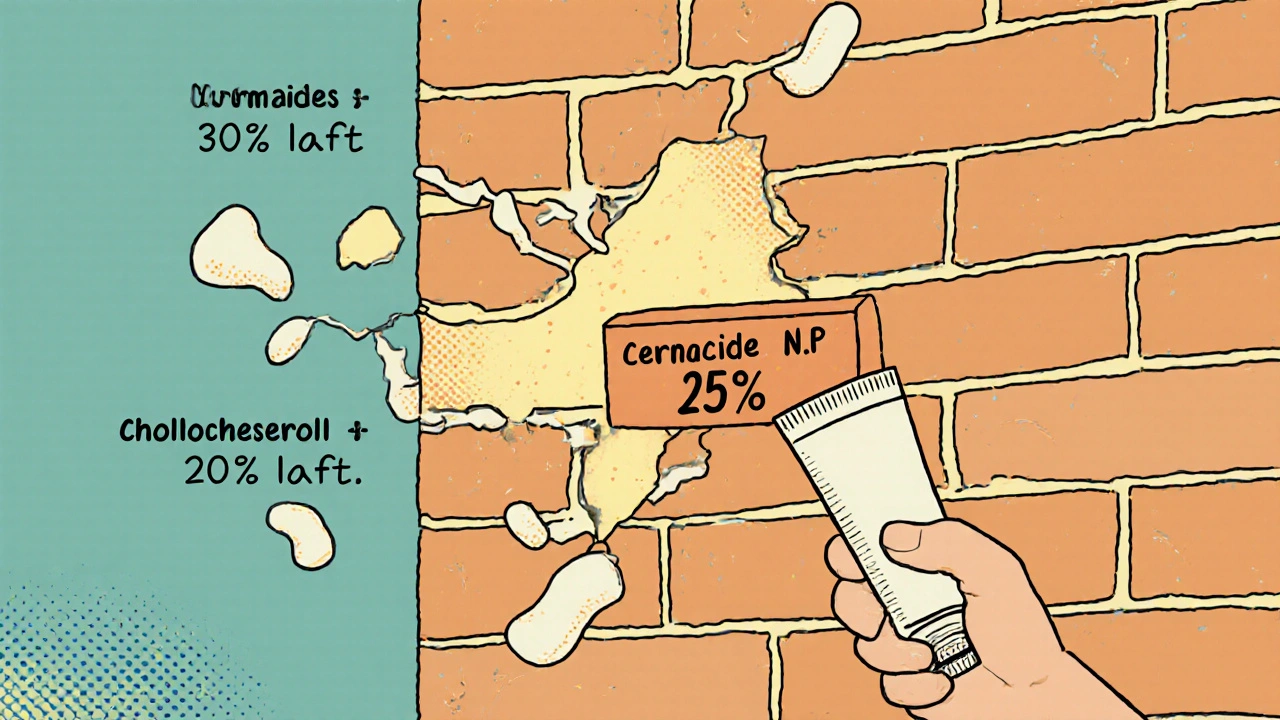
Ceramides restore the skin barrier in eczema by replacing missing lipids. Proper bathing-short, lukewarm soaks followed by immediate moisturizing-boosts results. Learn how to use ceramides effectively for lasting relief.
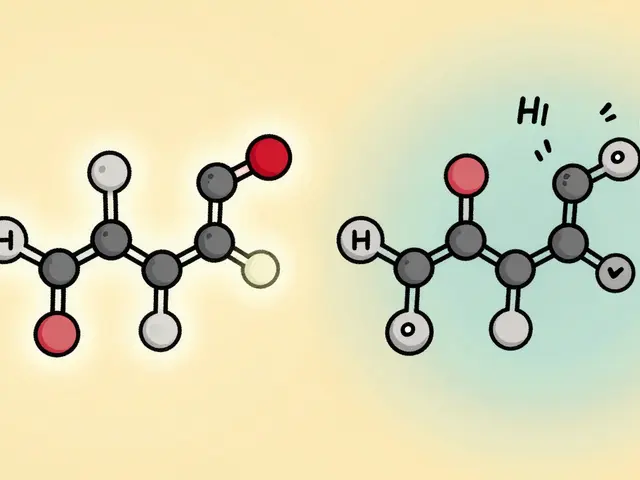
Cetirizine and levocetirizine both treat allergies, but levocetirizine causes less drowsiness. Learn why one might be better for daytime use and how to choose based on your needs.

Prevent seasonal depression with light therapy, vitamin D, and a consistent daily routine. Learn how to start early, use the right equipment, and build habits that keep your mood stable all winter.
Echinacea may seem like a safe immune booster, but for people on immunosuppressants, it can interfere with life-saving medications. Learn why experts warn against using it after transplants or for autoimmune conditions.
A side‑by‑side look at Cyclogyl (cyclopentolate) versus other mydriatic eye drops, covering onset, duration, safety, cost and best‑use scenarios.
Topical steroids treat eczema and psoriasis effectively but can cause skin thinning if misused. Learn how to use them safely with the right dose, duration, and strength to avoid permanent damage.