When you take two or more drugs at once, something unexpected might happen inside your body—this is called a drug interaction, a reaction between medications that changes how they work, increases side effects, or reduces their effectiveness. Also known as medication interactions, these aren’t rare accidents—they happen every day, often without people realizing it. One pill might make another stronger, weaker, or even toxic. It’s not just about prescription drugs. Over-the-counter painkillers, herbal supplements, and even your morning cup of coffee can trigger a reaction.
Most drug interactions happen because of how your liver processes medicines. The CYP3A4, a key enzyme in the liver that breaks down more than half of all common medications can be slowed down or sped up by other substances. Take grapefruit juice with certain blood pressure pills? That juice blocks CYP3A4, letting too much drug build up in your system. Or mix an antibiotic with a birth control pill? That could make the pill less effective. Then there’s pharmacokinetic interactions, how drugs affect each other’s absorption, movement, and breakdown in your body. And don’t forget pharmacodynamic interactions—when two drugs hit the same target in your brain or heart and amplify each other’s effects, like mixing sedatives and alcohol.
Some people are more at risk. Older adults on five or more meds? High risk. People taking drugs with a narrow therapeutic index—like warfarin or levothyroxine—where tiny changes in dose cause big problems? Even higher risk. And it’s not always obvious. You might feel dizzy, nauseous, or just "off," but never connect it to that new supplement you started. The good news? Most dangerous interactions are preventable. Pharmacists can spot them. Apps and clinician portals now flag risks in real time. And knowing what to ask—like "Could this new pill mess with my other meds?"—can save you from a hospital visit.
Below, you’ll find real-world examples of how common drugs clash—from kombucha and antidepressants to calcium and osteoporosis pills. You’ll learn why timing matters, why generics sometimes cause unexpected reactions, and how to avoid hidden dangers in your medicine cabinet. This isn’t theory. These are the exact situations people face every day. Let’s make sure you’re not one of them.

Benzodiazepines like Xanax and Ativan work fast for anxiety but carry serious risks when mixed with opioids, alcohol, or sleep meds. Learn the real dangers, safe alternatives, and what to do if you're already on one.

A clear comparison of Cleocin Gel (clindamycin) with other topical acne treatments, covering how they work, price, side effects, and tips for choosing the best option.
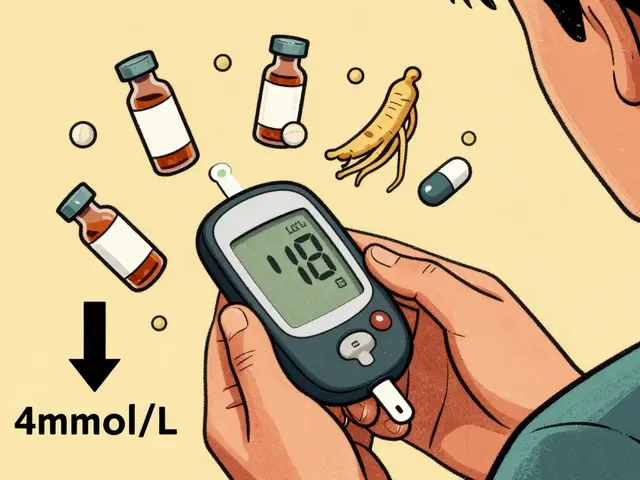
Ginseng may help lower blood sugar in type 2 diabetes, but it can dangerously interact with insulin and oral meds. Learn how to monitor your levels, avoid risks, and use it safely if approved by your doctor.

The nocebo effect explains why people feel side effects from medications even when the drug has no active ingredient. Expectations, not chemistry, often drive these reactions - and they're more common than you think.

Learn how to tell bacterial and viral infections apart, why antibiotics don't work on viruses, and what treatments actually help. Stop unnecessary antibiotic use and protect yourself from superbugs.

Learn how to safely buy cheap generic warfarin online in the UK, compare prices, verify reputable pharmacies, and manage dosage with INR monitoring.