When your blood sodium drops too low, it’s called hyponatremia, a condition where sodium levels in the blood fall below 135 mEq/L, disrupting fluid balance and nerve function. Also known as low sodium, it’s not just a lab number—it can cause confusion, seizures, or even coma if ignored. Many people think drinking more water fixes everything, but that’s often the opposite of what you need. Hyponatremia isn’t one problem—it’s a symptom of something deeper: heart failure, kidney disease, hormone imbalances, or even overhydration from too much water or certain meds like SSRIs.
How you treat it depends entirely on what’s causing it. If your body is holding onto too much water, you might need to fluid restriction, a simple but strict limit on daily water intake, often under 1 liter per day. If your adrenal glands aren’t making enough cortisol, you’ll need hormone replacement, typically with fludrocortisone or hydrocortisone to restore sodium balance. For severe cases, doctors use hypertonic saline—concentrated salt solution—slowly, because rushing it can damage your brain. And if a drug like hydrochlorothiazide or desmopressin is the culprit, stopping or switching it might be the best fix.
What you won’t find in most guides: the real-world messiness. Some people with chronic hyponatremia live fine with mild symptoms, while others crash fast. Older adults are at higher risk, especially if they take diuretics or have depression. Athletes who drink too much water during marathons? That’s a classic case. And here’s the kicker: some treatments that seem logical—like giving salt tablets—can make things worse if you don’t know the root cause. That’s why testing for urine sodium, osmolality, and volume status isn’t optional—it’s critical.
You’ll find posts below that dig into how medications like amitriptyline or diuretics can trigger sodium imbalances, how diet and fluid habits play a role, and what alternatives exist when standard treatments fail. No theory. No fluff. Just what doctors and patients actually deal with.
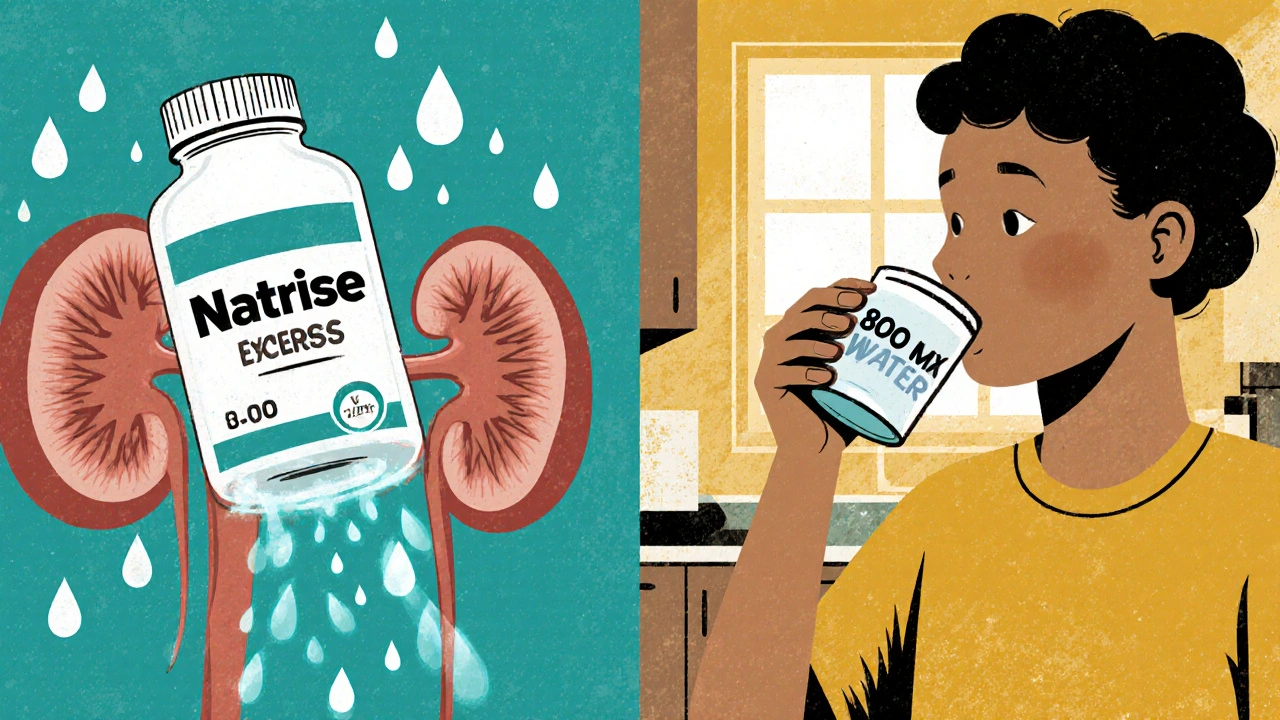

Natrise (tolvaptan) raises sodium levels fast but carries liver risks and high costs. Learn how fluid restriction, urea, demeclocycline, and salt tablets compare as safer, cheaper alternatives for hyponatremia.
Explore how Olmesartan/Amlodipine evolved, its clinical impact, and future developments in hypertension therapy.

What androstenedione does, what studies show, real risks, and 2025 legal status. Clear, science-based guide with safer alternatives and a quick checklist.
Multiple drug overdoses are deadly because substances interact unpredictably. Learn how naloxone, acetylcysteine, and emergency protocols work together to save lives when opioids, acetaminophen, or benzodiazepines are mixed.
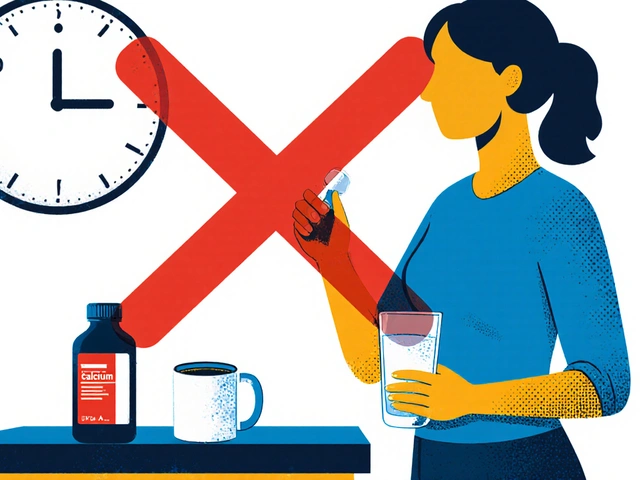

Learn how to take calcium supplements and bisphosphonates correctly to avoid absorption problems. Follow exact timing rules to maximize osteoporosis treatment and prevent fractures.
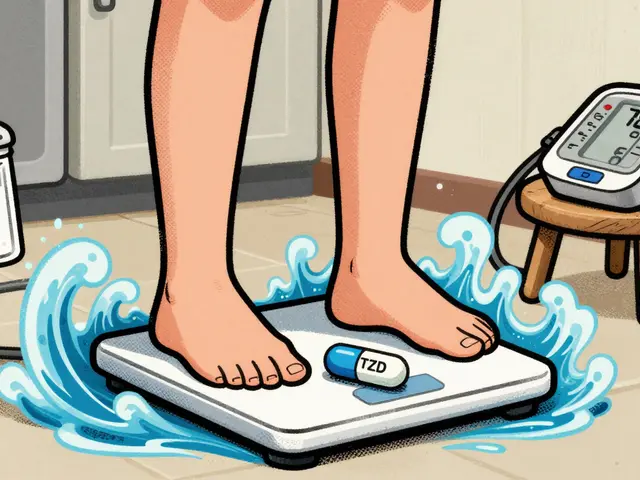

TZDs like pioglitazone help control blood sugar but often cause weight gain and swelling. Learn proven strategies to reduce fluid retention, lower doses safely, and combine with better alternatives like SGLT2 inhibitors.