When people talk about Elavil, a tricyclic antidepressant originally developed in the 1960s and still widely used today. Also known as amitriptyline, it works by balancing brain chemicals like serotonin and norepinephrine to ease depression, anxiety, and even chronic nerve pain. Unlike newer antidepressants, Elavil doesn’t just lift mood—it can also quiet down persistent pain signals, which is why doctors still prescribe it for conditions like fibromyalgia, diabetic neuropathy, and migraines.
But Elavil isn’t the only option. Many people switch to SSRIs, like fluoxetine or sertraline, which have fewer side effects and are easier to tolerate when they struggle with dry mouth, drowsiness, or weight gain from Elavil. Others turn to SNRIs, such as duloxetine or venlafaxine, which target the same brain pathways but with a cleaner profile. For nerve pain specifically, some find better results with gabapentin or pregabalin, which were designed for that purpose and rarely cause the sedation Elavil brings. Even though Elavil is cheap and effective, its side effect profile makes it a second-line choice for many today.
What’s interesting is how often Elavil shows up in unexpected places. It’s not just for depression—it’s used off-label for insomnia, irritable bowel syndrome, and even bedwetting in kids. That’s because its anticholinergic effects slow down overactive nerves and calm the nervous system. But that same mechanism causes the trade-offs: blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention, and next-day grogginess. People who’ve tried it often say the first week is brutal, but if they stick with it, the pain or sleep issues improve. Others quit fast because the side effects feel worse than the problem they’re trying to fix.
If you’re on Elavil right now, you’re not alone. Millions have used it, and many have found better options. The posts below dig into real comparisons—how it stacks up against other tricyclics like nortriptyline, what newer drugs replace it for pain or sleep, and how to safely taper off if you’re ready to move on. You’ll also find stories from people who tried alternatives and what actually worked for their bodies. No fluff. Just facts, trade-offs, and what to ask your doctor next.
Elavil (amitriptyline) is still used for pain, sleep, and depression, but many patients seek alternatives due to side effects. Compare duloxetine, pregabalin, mirtazapine, SSRIs, and non-drug options to find what works best for you.
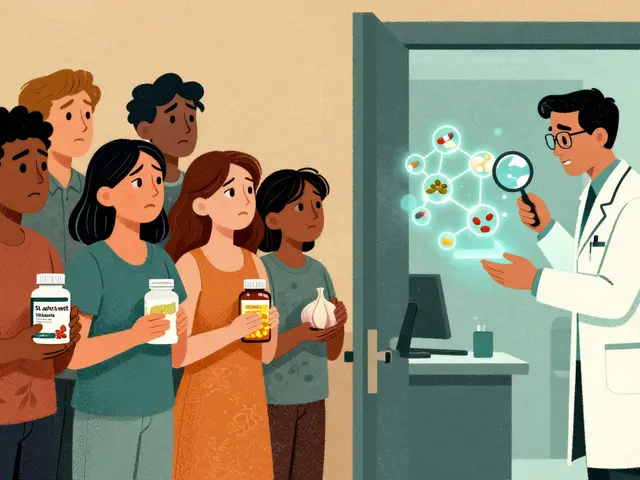

Most people don't tell their doctors about dietary supplements-even though they can interact dangerously with medications. Learn why full disclosure matters, which supplements are riskiest, and how to talk to your care team safely.
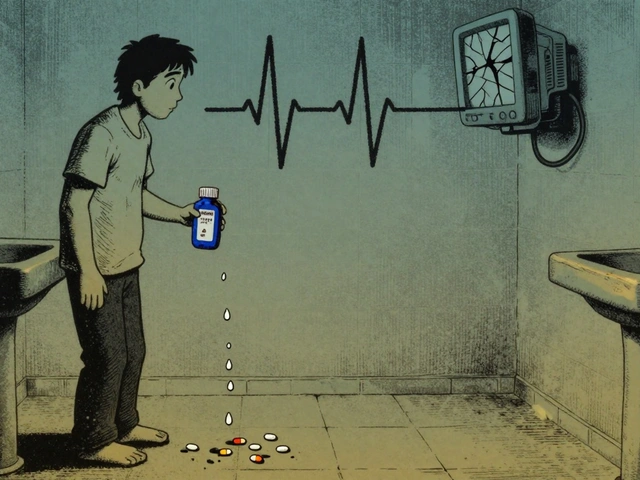
Loperamide, found in OTC antidiarrheals like Imodium, is being misused by people trying to self-treat opioid withdrawal. At high doses, it causes life-threatening heart rhythms and can be fatal. Learn the warning signs and why this isn't just another drug trend.
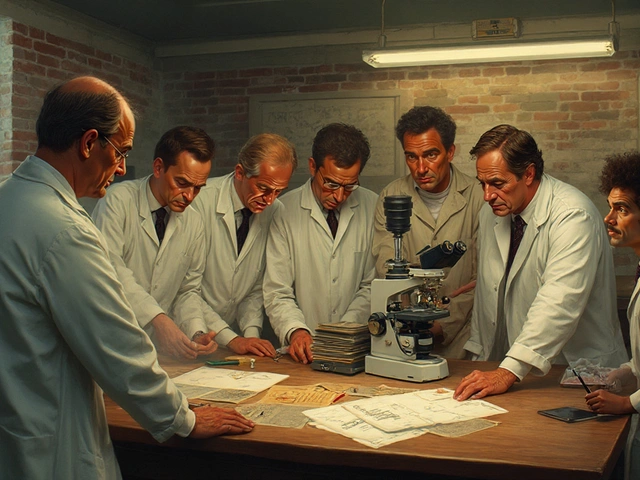

Trace the journey of HIV from its 1980s discovery to today’s advanced antiretroviral treatments, highlighting key milestones, scientists, and breakthroughs.

Acetaminophen combination products like Vicodin and Percocet can cause silent liver damage when taken with other meds. Learn how to avoid overdose, recognize risks, and use safer pain management strategies.

A clear, side‑by‑side comparison of Decadron (dexamethasone) and common steroid alternatives, covering potency, dosing, uses, side‑effects, and safety tips.