When working with Combination Therapy, the strategic use of two or more drugs or treatments together to tackle a disease. Also known as dual therapy, it aims to improve efficacy, reduce resistance, or balance side‑effects. In everyday practice you’ll see it pop up for cancer, infections, hypertension, and even mental health, where a single agent rarely does the whole job.
The first hurdle any clinician faces is Drug Interaction, the way two medicines influence each other’s absorption, metabolism, or action. Ignoring these links can turn a helpful duo into a harmful combo. Modern electronic prescribing tools flag risky overlaps, but the real skill lies in understanding the underlying enzymes, such as CYP450, that drive the interaction. By mastering this, you can safely pair a blood thinner with an antihypertensive or combine an antibiotic with a probiotic to protect gut health.
Another pillar is Personalized Medicine, the practice of tailoring treatment plans to a patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and comorbidities. When you match a genotype to a drug‑combo, you boost success rates dramatically. For example, pharmacogenomic testing can tell whether a patient will tolerate a dual antiretroviral regimen or need dose adjustments to avoid toxicity. This approach turns combination therapy from a one‑size‑fits‑all guess into a data‑driven strategy.
Evidence for any combo comes from Clinical Trials, controlled studies that test safety and efficacy of treatment protocols. Researchers design multi‑arm trials to compare monotherapy, dual therapy, and triple therapy side by side. The results often reveal that a carefully chosen pair can cut treatment time in half while keeping side‑effects low. Keeping up with recent trial data helps clinicians replace outdated regimens with newer, proven combos.
All these pieces—managing drug interactions, applying personalized medicine, and consulting trial results—fit together like a puzzle. When you put them in the right order, combination therapy becomes a powerful tool rather than a gamble. Below you’ll find articles that break down specific drug pairs, dive into genetics‑guided dosing, and highlight the latest trial outcomes, giving you a ready‑to‑use toolbox for everyday prescribing.
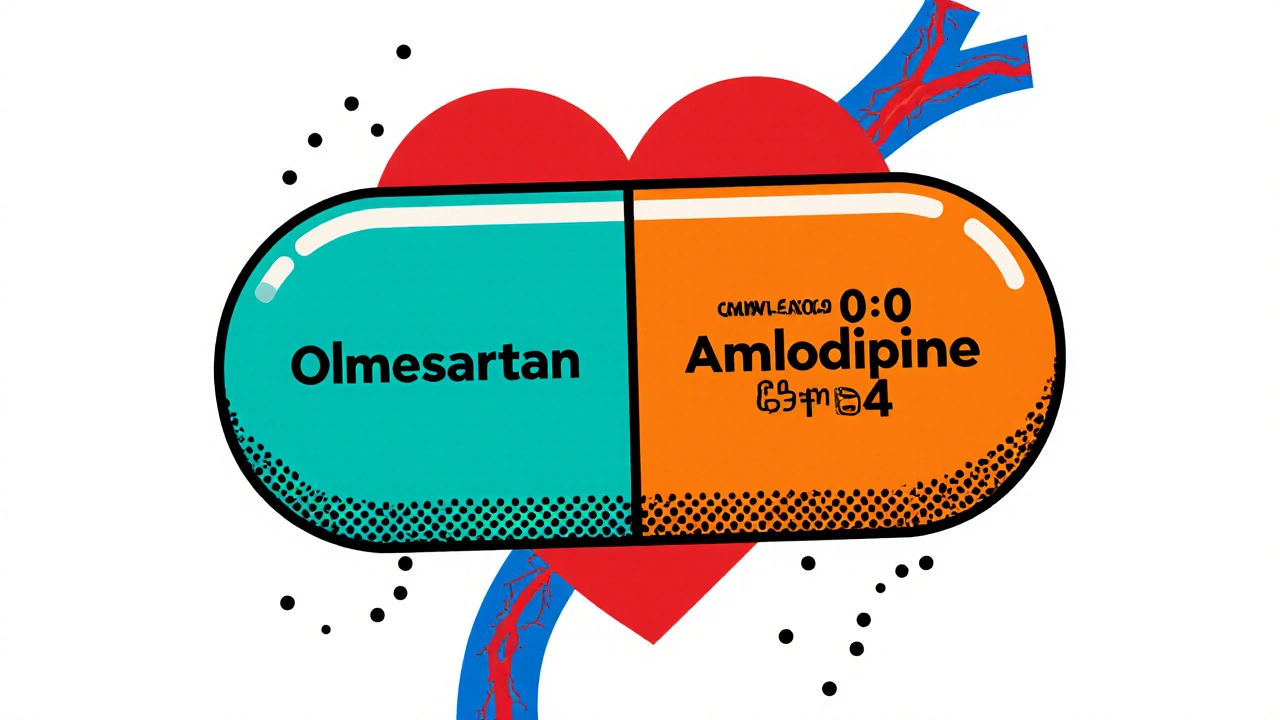
Explore how Olmesartan/Amlodipine evolved, its clinical impact, and future developments in hypertension therapy.
Compare Nexium (esomeprazole) with generic alternatives like omeprazole, lansoprazole, and pantoprazole. Learn which PPI works best for acid reflux, how to switch safely, and when lifestyle changes can replace medication.
Explore the latest research, new formulations, and future directions for metoclopramide, including safety updates, combination therapies, and personalized dosing.

What androstenedione does, what studies show, real risks, and 2025 legal status. Clear, science-based guide with safer alternatives and a quick checklist.

Learn how drug take-back programs safely dispose of unused medications through permanent drop boxes, mail-back envelopes, and nationwide events. Find out what you can and can’t dispose of, and how to locate the nearest collection site.

The nocebo effect explains why people feel side effects from medications even when the drug has no active ingredient. Expectations, not chemistry, often drive these reactions - and they're more common than you think.