When two or more drugs act on the same part of your body, they can either boost each other’s effects, cancel them out, or create unexpected reactions—that’s what we call pharmacodynamic interactions, when drugs affect each other’s action at the target site in the body, not through absorption or metabolism. Also known as drug interaction at the receptor level, these changes happen even if your body processes each drug perfectly. This isn’t about one drug blocking another from being absorbed. It’s about what happens after they’re already in your system—like when a sedative and an opioid both slow your breathing, or when two blood pressure meds drop your pressure too far.
These interactions are why some people feel dizzy after mixing a cold medicine with an antidepressant, or why older adults on multiple pills suddenly fall more often. Take sedating antihistamines, medications like diphenhydramine that cross the blood-brain barrier and cause drowsiness. When combined with opioids, benzodiazepines, or even some antidepressants, their combined effect on the central nervous system can be dangerous. That’s exactly why the Beers Criteria warns against them in seniors. Or look at ramipril, an ACE inhibitor used to lower blood pressure. Taking it with NSAIDs like ibuprofen can reduce its effect and harm your kidneys—something you won’t see on the bottle, but your doctor should know.
Pharmacodynamic interactions don’t always mean danger. Sometimes they’re designed. Combination pills like Olmesartan/Amlodipine, a blood pressure combo that targets two different pathways work because their effects add up safely. But when you’re mixing over-the-counter meds, supplements, or herbal products with prescriptions, you’re playing with untested combinations. That’s why so many posts here focus on alternatives—like swapping amitriptyline for duloxetine, or choosing tadalafil over other ED drugs with fewer interaction risks. You’re not just looking for what works—you’re looking for what works without turning your body into a battlefield.
What you’ll find below aren’t just articles about single drugs. They’re real-world guides to how drugs behave together. From calcium and bisphosphonates clashing over absorption, to tolvaptan’s liver risks when paired with other kidney-affecting meds, each post breaks down the hidden connections between what you take and how your body responds. No theory. No fluff. Just what you need to know to stay safe.
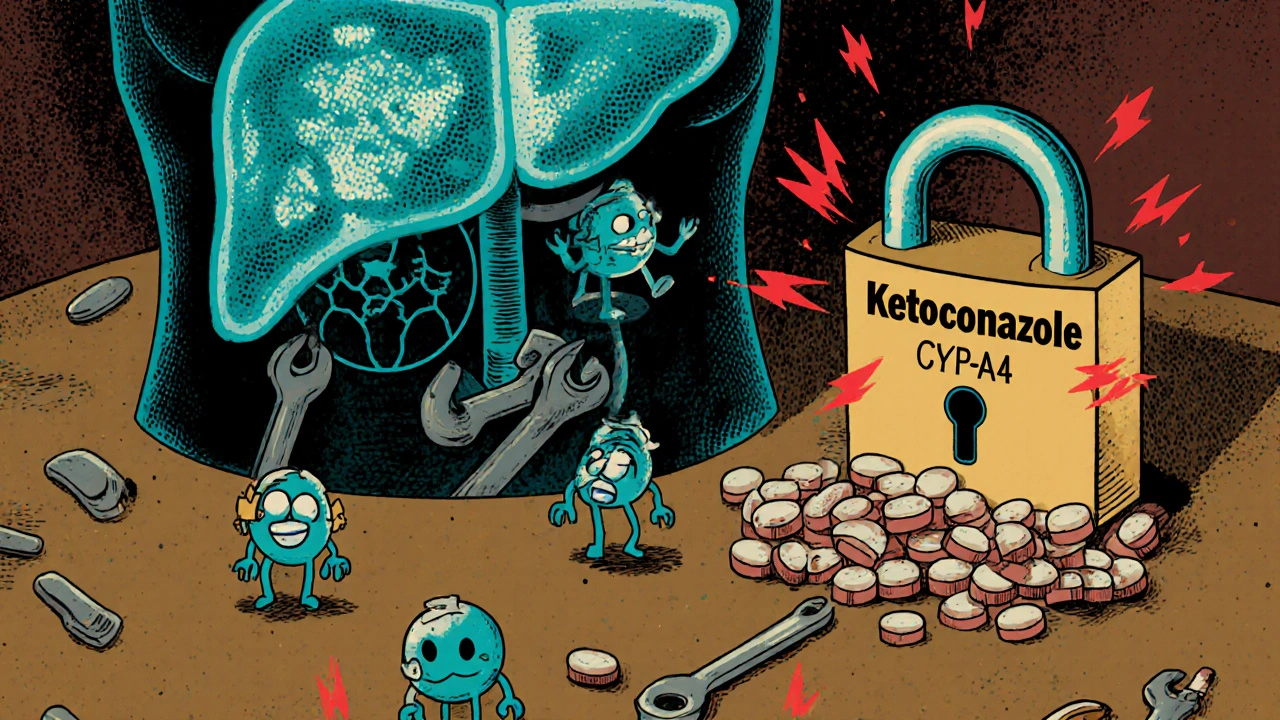
Drug-drug interactions can cause serious harm when medications clash in your body. Learn how liver enzymes, transporters, and genetics affect drug safety, and what you can do to avoid dangerous combinations.

A practical guide comparing Modvigil (modafinil) with armodafinil, adrafinil, Provigil and caffeine‑L‑theanine, covering cost, duration, safety and best use cases.

This easy-to-read guide explains in plain language how levetiracetam controls seizures, making it accessible for patients and caregivers. It covers what levetiracetam does in the brain, how it helps people with epilepsy, what side effects to look for, and tips to get the most out of the medication. You'll learn what to expect and get practical advice, plus a helpful resource for understanding how levetiracetam works.

A comprehensive side‑by‑side comparison of female Viagra (sildenafil) with Addyi, Vyleesi, generic options and herbal alternatives, covering how they work, dosing, safety and when each is best.

A detailed comparison of Sinemet with other Parkinson's medications, covering benefits, drawbacks, costs, and when to switch for optimal symptom control.

Kombucha contains trace alcohol that can interact dangerously with medications like metronidazole, SSRIs, and diabetes drugs. Learn what levels are safe, how to spot risky products, and what to do if you're on alcohol-sensitive meds.