When you hear interchangeable biosimilars, a type of biologic medication approved by the FDA to be substituted for the original brand drug without needing a doctor’s reauthorization. Also known as biosimilar substitutes, they’re not just cheaper copies—they’re scientifically matched versions of complex, living-cell-derived drugs like Humira or Enbrel. Unlike regular generics, which are simple chemical copies, biosimilars come from living organisms, making them far harder to replicate exactly. But when a biosimilar gets the "interchangeable" label, it means the FDA has confirmed you can switch between it and the original drug as easily as you would between two brands of aspirin—no extra paperwork, no doctor’s note, no risk.
This matters because biologics can cost over $100,000 a year. Many patients can’t afford them, and insurers won’t cover them without alternatives. biosimilars, medications that are highly similar to an already-approved biologic but not identical. Also known as biologic generics, they’ve been around since 2015, but only a handful have reached the interchangeable status. That’s changing fast. The FDA has been tightening its standards, requiring real-world data showing no increased risk of side effects or reduced effectiveness when patients switch. FDA biosimilar approval, the process by which the U.S. Food and Drug Administration evaluates and authorizes biosimilar and interchangeable biologics for market. Also known as biologics license application pathway, it’s now the key gatekeeper for cost savings across diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer treatments. And while some doctors still hesitate to switch patients, studies show no difference in outcomes when patients are moved from Humira to its interchangeable biosimilar—over 10,000 patients tracked across multiple trials.
But here’s the catch: not all biosimilars are interchangeable. Many are approved as "biosimilar" only, meaning your pharmacist can’t swap them without your doctor’s okay. That’s why understanding the difference matters when you’re filling a prescription. It’s also why some patients report side effects after switching—sometimes it’s the inactive ingredients, sometimes it’s the nocebo effect, and sometimes it’s just bad luck with a particular batch. The drug substitution, the practice of replacing a prescribed medication with a chemically or biologically similar alternative. Also known as pharmaceutical substitution, it’s the backbone of savings in modern healthcare. But it only works if you trust the system. And that’s why the posts below dig into real cases: why some people react differently to biosimilars, how the FDA tracks safety after approval, what happens when a drug is switched mid-treatment, and why some insurers still block the cheapest option—even when it’s officially interchangeable.
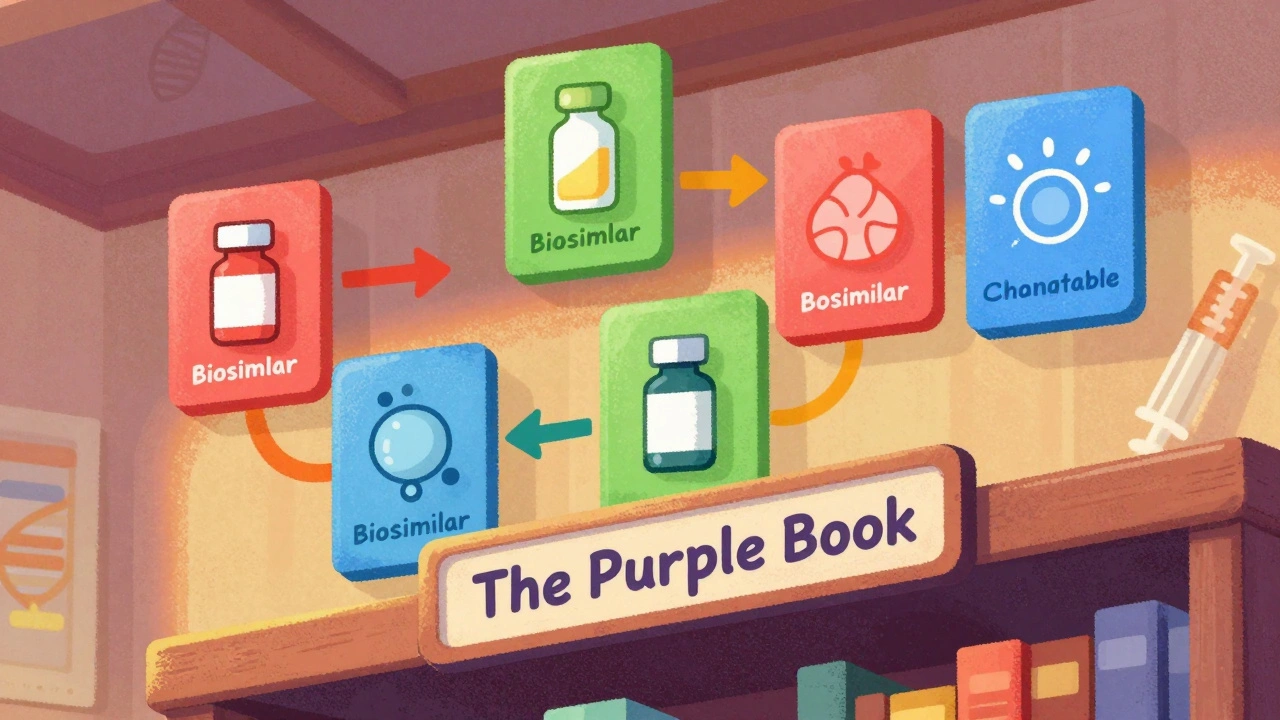
The FDA's Purple Book is the official guide to biosimilars and interchangeable biological drugs. Learn how it works, what the difference is between biosimilars and interchangeable products, and how pharmacists use it to make safe substitutions.

When drugs are unavailable due to shortages or allergies, compounding pharmacies offer customized solutions-like allergen-free pills, flavored liquids for kids, or topical gels. Learn how they work, when to use them, and what to ask before starting.

Navigating premature ejaculation in 2025 offers more options than ever before. This article explores eight alternatives to Priligy, highlighting the pros and cons of each. From psychotherapy to natural remedies, find out what might work best for you. Our insights include practical tips and interesting facts, aiming to support your journey toward better sexual health.

Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) plays a pivotal role in bile acid metabolism, offering numerous benefits for individuals with liver health concerns. It's fascinating how this substance can improve the breakdown and absorption of dietary fats and vitamins. For those grappling with liver disorders, understanding UDCA's impact is key to better health outcomes. This article explores the science behind UDCA, its practical advantages, and offers tips for maximizing its benefits.

Dizziness after surgery can be a common yet disorienting experience. This piece explores practical ways to manage dizziness effectively, delving into causes and offering helpful tips for recovery. Understanding how to navigate these post-surgery effects is key to a smoother healing process. Learn what to expect and how to ease this sensation in everyday life.
Pitavastatin is a cholesterol-lowering drug with a lower risk of increasing diabetes compared to other statins. Research shows it's a safer option for people with prediabetes, though cost and access can be barriers. Learn how it stacks up against common alternatives and what experts recommend.