Did you know that beta blockers can cut heart attack risk by up to 30%? That’s why doctors prescribe them for high blood pressure, angina, and irregular beats. But not every beta blocker works the same way, and picking the wrong one can bring unwanted side effects.
Beta blockers block the adrenaline receptors (beta‑1 and beta‑2) in your heart and blood vessels. By doing that, they slow your heartbeat, lower blood pressure, and reduce the heart’s workload. Some drugs focus mainly on the heart (beta‑1 selective), while others affect both heart and lungs (non‑selective). The difference matters if you have asthma, diabetes, or need a fast‑acting pill.
When you start a beta blocker, expect a gradual drop in pulse and blood pressure over a few days. Most people feel steadier, but a few notice fatigue, cold hands, or a mild drop in exercise tolerance. Those symptoms usually fade as your body adjusts.
1. Metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol‑XL) – Beta‑1 selective, works well for high blood pressure and post‑heart‑attack care. It’s available in immediate and extended‑release forms. Side effects are mild for most, but watch for insomnia or vivid dreams.
2. Atenolol (Tenormin) – Another beta‑1 selective option, popular for hypertension. It’s cheap and once‑daily, but can cause more fatigue than metoprolol, especially in older adults.
3. Carvedilol (Coreg) – Non‑selective with added alpha‑blocking properties, which also dilates blood vessels. Great for heart failure, but may cause dizziness when you stand up quickly.
4. Propranolol (Inderal) – Classic non‑selective blocker, used for migraines, tremors, and anxiety as well as heart issues. Because it hits the lungs, it’s not ideal for asthma sufferers.
5. Nebivolol (Bystolic) – Newer beta‑1 selective drug that also releases nitric oxide, helping vessels relax. It’s gentle on the lungs and may improve blood flow, making it a good pick for patients with mild COPD.
Which one fits you? If you have asthma, stick to beta‑1 selective agents like metoprolol or nebivolol. For heart failure, carvedilol’s extra vasodilation often wins. If you need migraine relief, propranolol is the go‑to.
Dosage matters too. Doctors usually start low and increase slowly to avoid a sudden dip in blood pressure. Never stop a beta blocker abruptly—your heart can react with a rapid spike in rate and blood pressure.
To sum up, beta blockers are powerful tools, but the right choice depends on your overall health, other meds, and how your body reacts. Talk with your doctor about any lingering fatigue, cold extremities, or breathing troubles, and they can tweak the drug or dose.
Armed with this quick comparison, you can ask smarter questions at your next appointment and feel confident that you’re on the best beta blocker for your needs.
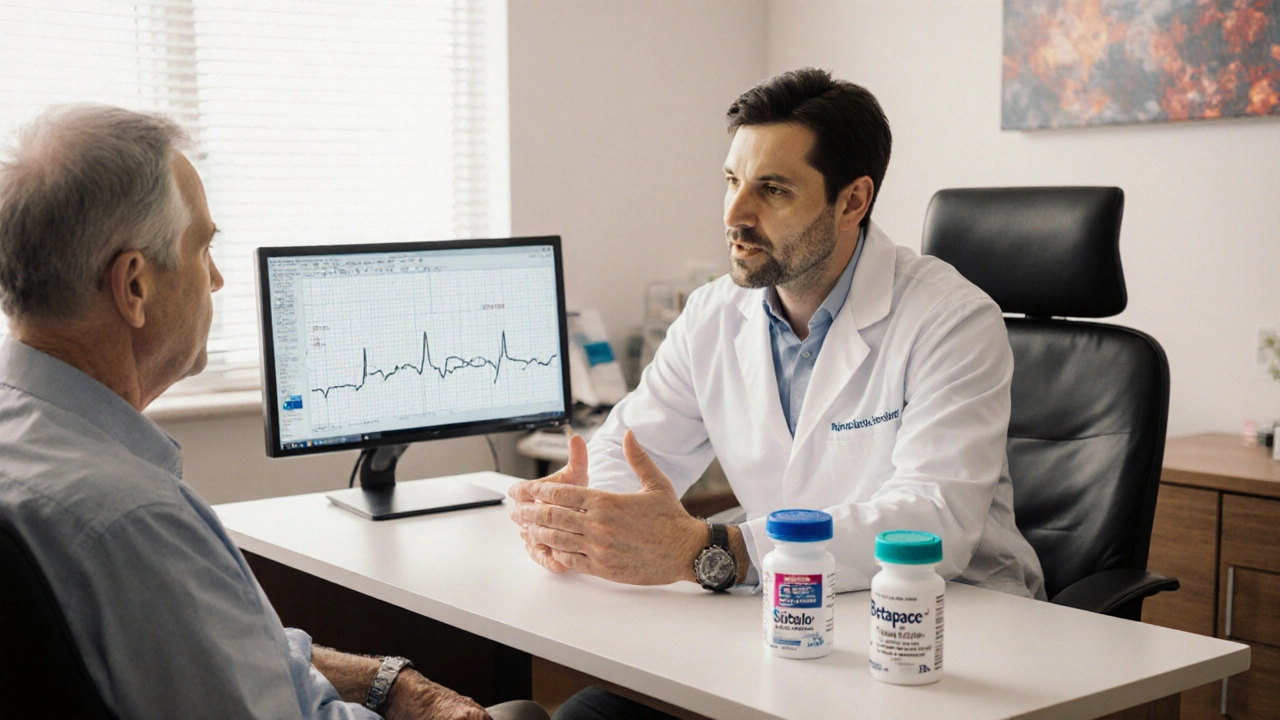

Compare Betapace (sotalol) with top anti‑arrhythmic alternatives, covering mechanisms, dosing, side effects, and when to choose each.

The FDA uses Import Alerts to automatically block drug shipments from non-compliant manufacturers. With the 2025 Green List initiative, enforcement against GLP-1 APIs has become the strictest in history-reshaping global supply chains and raising compliance standards.
Coronary artery disease, caused by atherosclerosis, is the leading cause of death worldwide. Learn how plaque builds up, who’s at risk, and what treatments actually work-based on the latest 2023 guidelines.
Loperamide, found in OTC antidiarrheals like Imodium, is being misused by people trying to self-treat opioid withdrawal. At high doses, it causes life-threatening heart rhythms and can be fatal. Learn the warning signs and why this isn't just another drug trend.
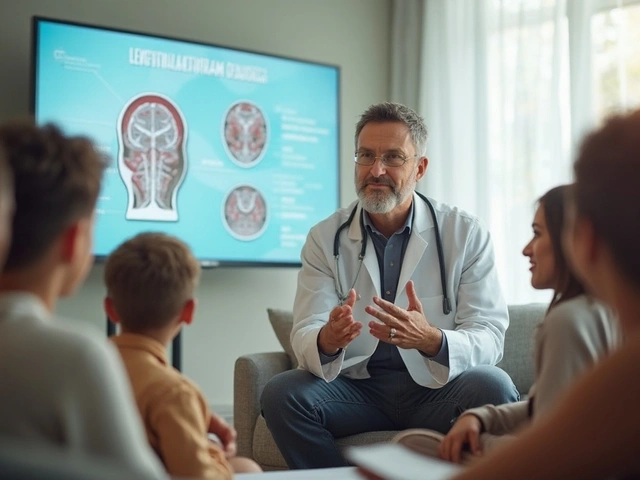

This easy-to-read guide explains in plain language how levetiracetam controls seizures, making it accessible for patients and caregivers. It covers what levetiracetam does in the brain, how it helps people with epilepsy, what side effects to look for, and tips to get the most out of the medication. You'll learn what to expect and get practical advice, plus a helpful resource for understanding how levetiracetam works.

Explore the complete journey of latanoprost-from its chemical breakthrough and clinical trials to FDA approval and its role in modern glaucoma therapy.