If your doctor has mentioned antiarrhythmic drugs but you’re worried about side effects, you’re not alone. Many people look for safer ways to keep their heart rhythm in check without jumping straight into powerful prescription meds. In this guide we’ll break down the most common alternatives, when they work best, and how to decide if they’re right for you.
Traditional antiarrhythmics—like amiodarone, sotalol, or flecainide—are effective, but they can also cause thyroid problems, lung issues, or interact with other medicines. Sometimes the risk outweighs the benefit, especially for mild to moderate arrhythmias. An alternative approach can lower that risk, improve quality of life, and still give you control over your heartbeat.
1. Lifestyle tweaks
Regular exercise, a balanced diet low in caffeine and alcohol, and stress‑reduction techniques (yoga, meditation, deep‑breathing) can calm the nervous system and reduce irregular beats. Even a short daily walk can make a big difference.
2. Over‑the‑counter supplements
Magnesium and potassium are essential minerals that help maintain a steady rhythm. A daily magnesium citrate (200‑400 mg) and potassium‑rich foods like bananas, spinach, and avocados can help prevent extrasystoles. Always check with a pharmacist if you’re on other meds.
3. Herbal helpers
Some herbs, such as hawthorn berry and mother‑wort, have mild cardioprotective effects. Hawthorn tea or standardized extracts may improve blood flow and support normal rhythm. Use reputable brands and avoid high doses without medical advice.
4. Wearable monitors
Devices like smart watches or dedicated ECG patches let you track your heartbeat in real time. Seeing patterns helps you spot triggers (like caffeine spikes) and share accurate data with your doctor.
5. Beta‑blocker alternatives
If a prescription is still needed, doctors often start with low‑dose beta‑blockers (e.g., metoprolol) because they’re easier on the body than stronger antiarrhythmics. They slow the heart just enough to prevent rapid beats without major organ toxicity.
6. Calcium‑channel blockers
Drugs like verapamil or diltiazem can also stabilize rhythm, especially for atrial fibrillation. They work by relaxing heart muscle and blood vessels, offering a gentler option for many patients.
7. Digoxin (in select cases)
While older, digoxin can be useful for certain types of atrial flutter. It requires careful blood‑level monitoring but may avoid the harsher side effects of newer antiarrhythmics.
Every alternative has pros and cons, and what works for one person might not work for another. The key is a step‑by‑step approach: start with lifestyle changes, add supplements if needed, and only move to prescription meds when those aren’t enough.
First, get a clear diagnosis. An ECG, Holter monitor, or event recorder will tell you the exact type of arrhythmia you have. Next, discuss your medical history—especially any thyroid, lung, or kidney issues—with your doctor. Ask about a trial of magnesium or a low‑dose beta‑blocker before considering stronger drugs.
Keep a symptom diary. Note when you feel palpitations, what you ate, how much you slept, and any stressors. Patterns often emerge that point to simple triggers you can eliminate.
If you decide to try an over‑the‑counter supplement, start low and watch for side effects like diarrhea (magnesium) or stomach upset (potassium). Report any new dizziness or fainting to your healthcare provider immediately.
Remember, the goal isn’t to avoid all medication but to find the safest, most effective way to keep your heart rhythm regular. Regular check‑ins with your doctor, honest reporting of symptoms, and a willingness to adjust your plan are the best tools you have.
By combining smart lifestyle choices, targeted supplements, and, when needed, gentle prescription drugs, most people can manage arrhythmias without the heavy side‑effect load of traditional antiarrhythmics. Talk to your doctor today about which alternatives fit your life best.
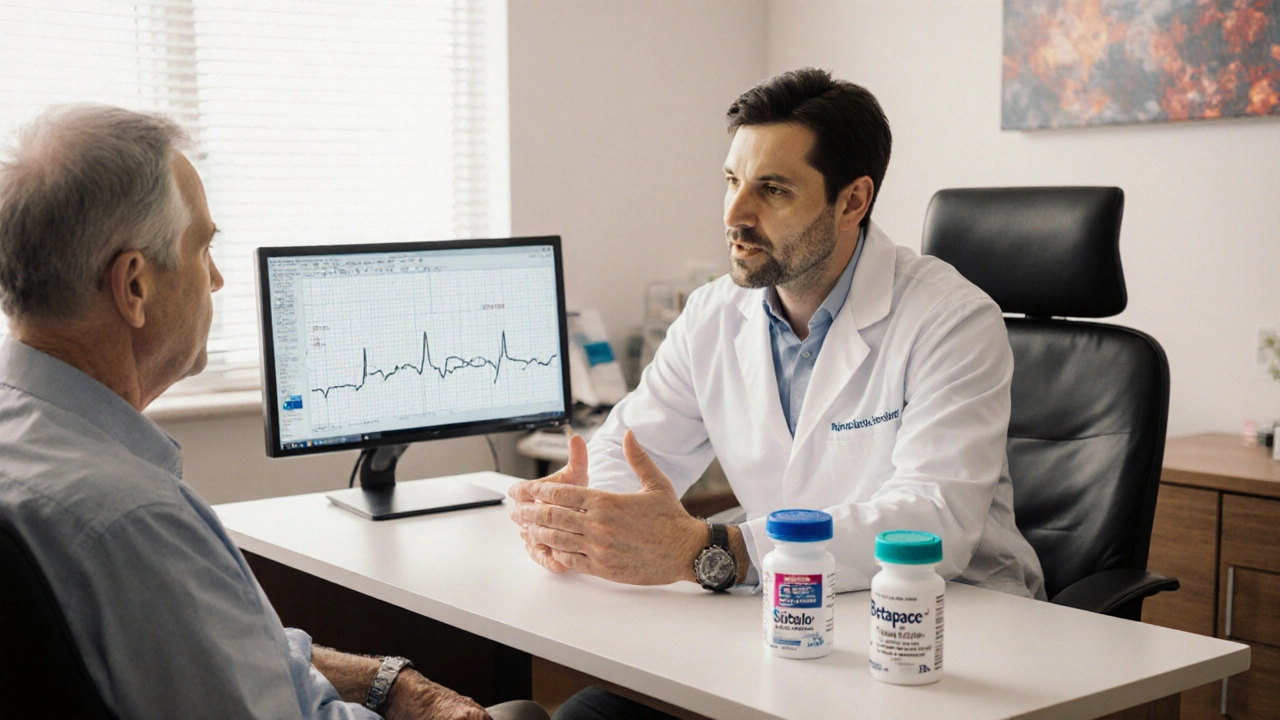

Compare Betapace (sotalol) with top anti‑arrhythmic alternatives, covering mechanisms, dosing, side effects, and when to choose each.

Explore how genetics, therapeutic monitoring, and new delivery methods can personalize ethambutol therapy, reduce eye toxicity, and boost TB treatment success.
Discover how to soothe tendonitis pain naturally with ice, heat, stretches, strengthening exercises, and anti‑inflammatory herbs for lasting relief.

Learn how cabergoline works for men, the conditions it treats, dosing tips, benefits, risks, and how it compares to other dopamine agonists.
Check your medicine cabinet twice a year to remove expired drugs and prevent accidents. Learn what to toss, where to store meds safely, and how to dispose of them the right way.
Explore why genotype 3 hepatitis C often causes stubborn fatigue, the biological reasons behind it, and practical steps to manage and recover from this symptom.