When your body holds onto too much water and your sodium levels drop dangerously low, Tolvaptan, a vasopressin receptor blocker used to treat hyponatremia and fluid overload in conditions like heart failure and liver cirrhosis. Also known as a ADH antagonist, it works by telling your kidneys to flush out extra water without losing sodium. Unlike diuretics that strip away both water and salt, Tolvaptan targets just the water—making it a precise tool for correcting electrolyte imbalances.
Tolvaptan doesn’t work for every kind of low sodium. It’s mainly used when the problem comes from the body’s own hormones—like too much antidiuretic hormone (ADH)—which tricks the kidneys into holding water. This happens in syndromes like SIADH, or in advanced heart and liver disease. It’s not a first-line fix for mild cases, but when other treatments fail or aren’t safe, Tolvaptan steps in. It’s also used in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) to slow cyst growth and preserve kidney function over time. The key? It’s not a quick fix. It’s a long-term medication that requires careful monitoring of sodium levels to avoid overcorrection, which can cause brain damage.
Related to Tolvaptan are other ways to manage fluid balance. Hyponatremia, a condition where blood sodium falls below 135 mmol/L, often caused by excess water retention or hormone imbalances can be treated with fluid restriction, salt tablets, or other drugs like demeclocycline. Kidney function, how well your kidneys filter waste and regulate fluids and electrolytes is central to understanding why Tolvaptan works—and why it can be risky if your kidneys are already damaged. And then there’s Vasopressin receptor blocker, the drug class Tolvaptan belongs to, which stops the hormone that tells kidneys to hold water. Other drugs in this class are still experimental or not widely available, making Tolvaptan one of the few real options.
People using Tolvaptan often need to track their urine output, weight, and blood tests closely. It’s not a drug you take casually. Side effects include extreme thirst, dry mouth, and in rare cases, liver injury. That’s why it’s usually reserved for patients who’ve tried other options and still struggle with fluid overload. Many users find themselves comparing it to loop diuretics like furosemide, but those don’t fix the root hormone problem—they just push out more fluid, often dragging sodium down with it. Tolvaptan does the opposite: it removes water while keeping sodium stable.
Below, you’ll find real-world comparisons and insights from people who’ve used Tolvaptan—or switched away from it. Whether you’re looking for alternatives, side effect reports, or how it stacks up against other kidney-focused treatments, the posts here give you the unfiltered details you won’t get from a drug label. No fluff. Just what works, what doesn’t, and what to watch out for.
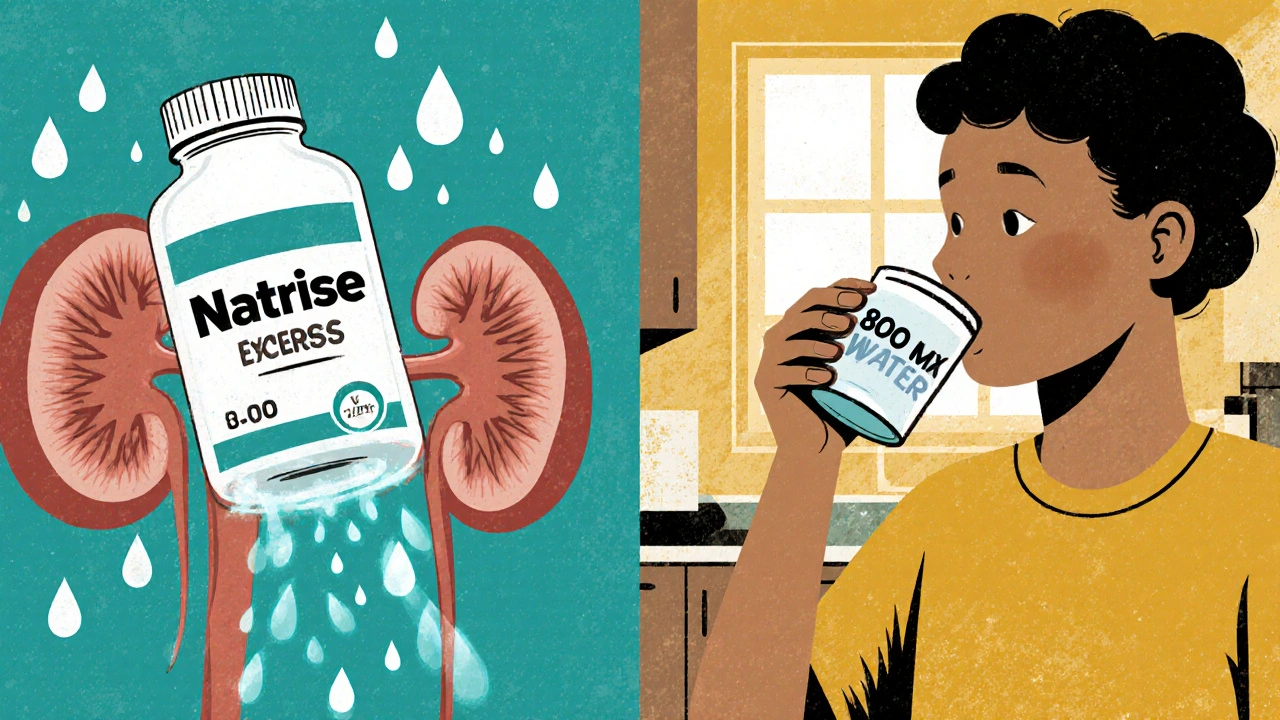

Natrise (tolvaptan) raises sodium levels fast but carries liver risks and high costs. Learn how fluid restriction, urea, demeclocycline, and salt tablets compare as safer, cheaper alternatives for hyponatremia.

Want generic Clomid cheap online? Here’s how to do it safely and legally in 2025-prices, telehealth, legit pharmacies, red flags, and smarter alternatives.

A comprehensive side‑by‑side comparison of female Viagra (sildenafil) with Addyi, Vyleesi, generic options and herbal alternatives, covering how they work, dosing, safety and when each is best.

Learn how progesterone affects gut motility, bile flow, and microbiome health, recognize deficiency signs, and discover natural and medical ways to improve digestion.
Infographics about generics help patients understand that generic drugs are just as safe and effective as brand-name versions. With clear visuals, they debunk myths, explain FDA approval, and show how generics save money-without sacrificing quality.

Prior authorization is a common but confusing step in getting your prescription covered by insurance. Learn what drugs require it, how the process works, what to do if it's denied, and how to avoid delays.