When dealing with immunosuppressants, drugs that intentionally reduce or block immune system activity. Also known as immune suppressive agents, they become necessary whenever the body’s own defenses threaten a medical goal.
Corticosteroids, synthetic versions of the hormone cortisol, act fast to calm inflammation and immune activation are often the first line after surgery or during an acute flare. Their quick effect makes them ideal for induction therapy, but long‑term use demands low dosing to avoid bone loss, diabetes, or weight gain. Calcineurin inhibitors, agents such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus that block a specific signaling enzyme in T‑cells provide deeper suppression for organ‑transplant patients. Monitoring blood levels is critical because the therapeutic window is narrow and kidney toxicity is a real risk.
Beyond these, Biologic agents, engineered proteins that target specific immune pathways like TNF‑α or IL‑6 have reshaped treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Their precision reduces broad‑scale immune shutdown, yet cost and infection risk keep them reserved for patients who don’t respond to older drugs. Understanding how immunosuppressants work helps patients and clinicians balance effectiveness with safety.
Immunosuppressants encompass multiple drug families, each with distinct mechanisms, side‑effect profiles, and monitoring needs. They require careful laboratory testing—liver enzymes for corticosteroids, trough levels for calcineurin inhibitors, and infection screening for biologics. Failure to follow protocols can lead to organ rejection, disease flare, or severe complications.
Autoimmune diseases influence immunosuppressant choice because the underlying pathology dictates which immune pathways are most harmful. For example, lupus patients often need a combination of steroids and antimetabolites, while transplant recipients rely heavily on calcineurin inhibitors to prevent graft loss. Matching the drug to the disease ensures the right amount of suppression without unnecessary toxicity.
Organ transplant is perhaps the most classic scenario for immunosuppressant use. After a kidney or liver transplant, a life‑long regimen of a calcineurin inhibitor, an antimetabolite, and low‑dose steroids is common. The goal is to keep the new organ alive while minimizing drug‑related damage. Patients must stay vigilant about infections, blood pressure, and kidney function—regular follow‑up visits become a routine part of life.
The articles below dive deeper into specific drugs, compare alternatives, and offer real‑world tips for dosing, side‑effect management, and cost‑saving strategies. Whether you’re starting a new regimen or looking to switch agents, the collection provides the practical insight you need to make informed decisions.

Echinacea may seem like a safe immune booster, but for people on immunosuppressants, it can interfere with life-saving medications. Learn why experts warn against using it after transplants or for autoimmune conditions.
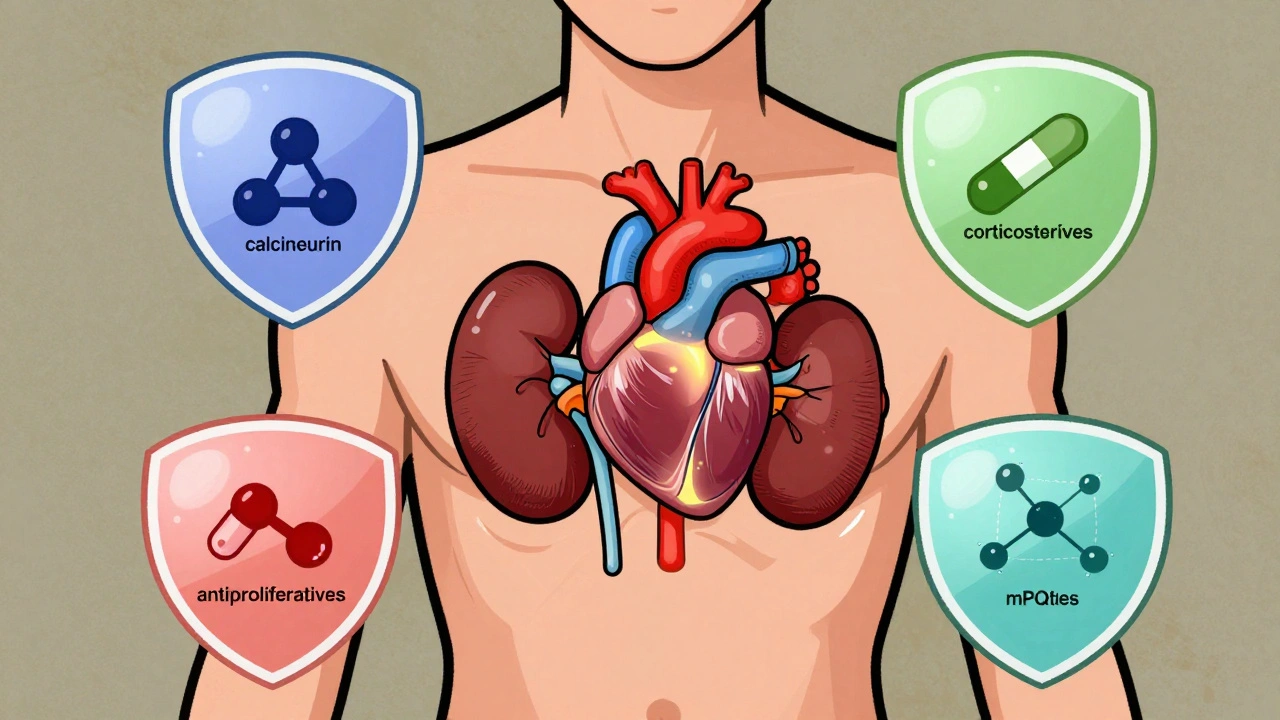
Immunosuppressants prevent organ rejection after transplant but carry serious risks like infection, cancer, and kidney damage. Learn how to manage these drugs safely, avoid missed doses, and reduce long-term side effects.
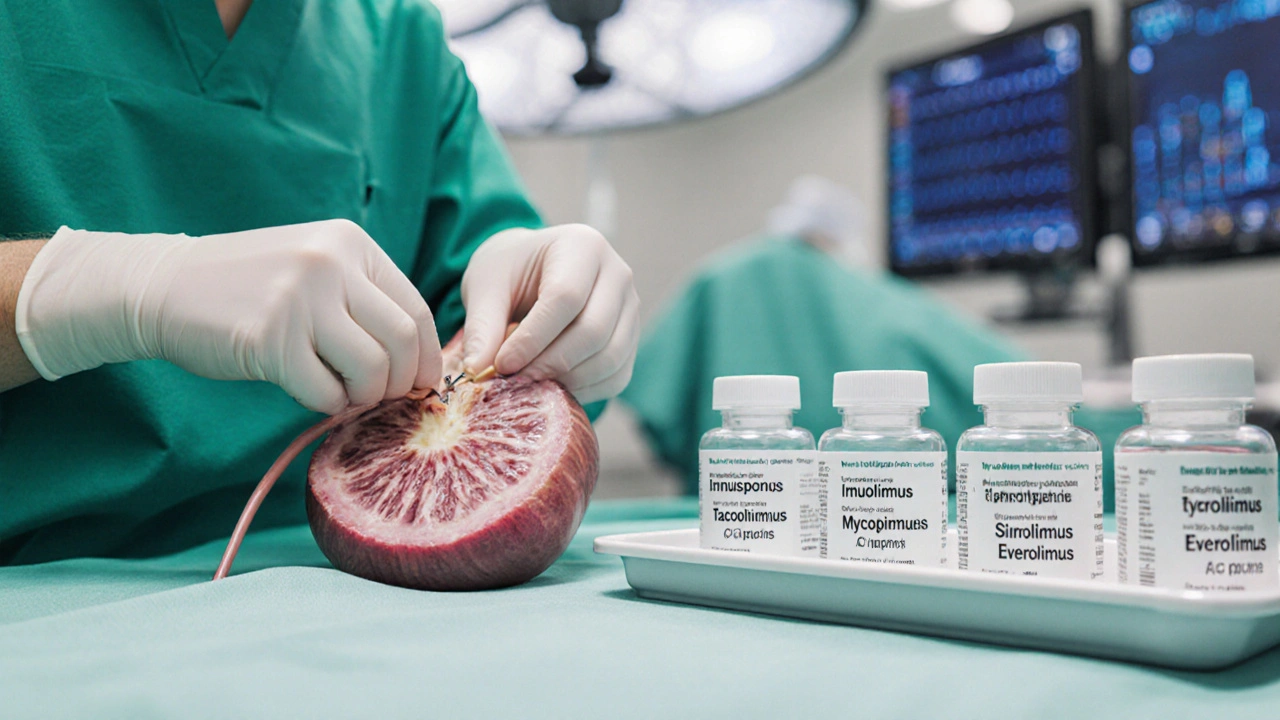
A side‑by‑side look at Imusporin (cyclosporine) versus tacrolimus, mycophenolate, sirolimus, everolimus and others, covering mechanisms, side effects, UK costs and when to switch.

SNRI medications offer a dual-action approach to treating depression and chronic pain by boosting serotonin and norepinephrine. Learn how they compare to SSRIs, their real-world effectiveness, side effects, and why they're a key option for treatment-resistant cases.
Learn how to manage hypoparathyroidism with calcium and vitamin D, including dosing, diet, monitoring, and when to consider newer PTH therapies. Avoid kidney damage and stabilize your symptoms with proven strategies.

Discover seven effective alternatives to Diclofenac in 2025. Each option is explored in terms of benefits and drawbacks, offering insight into modern pain management methods. Learn the unique features of each alternative, including their impacts on different types of pain and side effects. Whether you're managing chronic pain or seeking a safer medication, this guide provides valuable information for better health decisions.
Explore the latest research, new formulations, and future directions for metoclopramide, including safety updates, combination therapies, and personalized dosing.

Tired of Pharmex Direct or just curious about what else is out there? This article unpacks the best alternatives for Canadians looking for reliable pharmacy options. From big-brand stores to convenient online choices, get the details on pricing, services, and trustworthiness. For anyone who wants straightforward pharmacy solutions without the fuss, this will make picking your next pharmacy a whole lot easier.