If you or a loved one has been prescribed a heart drug, you probably have questions. What does the pill actually do? How often should you take it? Which side effects matter? This guide breaks down the basics so you can feel confident about your treatment and avoid common pitfalls.
Heart medicines fall into a few easy‑to‑remember groups. Each group targets a different problem that can strain the heart.
Beta‑blockers slow the heart rate and lower blood pressure. They’re often used after a heart attack or for chronic angina. Common names include metoprolol, atenolol, and carvedilol.
ACE inhibitors and ARBs relax blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump. Drugs like lisinopril, ramipril, and losartan are typical examples. They’re the go‑to choice for high blood pressure and heart failure.
Statins lower cholesterol, reducing the buildup of plaque in arteries. Atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin are among the most prescribed.
Anticoagulants thin the blood to prevent clots. Warfarin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban fall into this category. They’re crucial for atrial fibrillation and patients with artificial heart valves.
Diuretics help the body get rid of excess fluid, easing the workload on the heart. Furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide are common diuretics used in heart failure.
Taking heart medication isn’t just about swallowing a pill. Small habits can make a big difference in how well the drug works and how few side effects you feel.
Follow the timing. Some meds work best with food, others on an empty stomach. Read the label or ask your pharmacist. For example, many statins are taken at night because the liver makes most cholesterol while you sleep.
Never skip doses. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember—unless it’s almost time for the next one. Doubling up can raise the risk of low blood pressure or dangerous heart rhythms.
Watch for interactions. Over‑the‑counter pain relievers, herbal supplements, and even certain foods can interfere with heart drugs. Grapefruit juice, for instance, can raise levels of some statins and cause muscle pain.
Keep a medication list. Write down each drug, dose, and why you’re taking it. Share this list with every doctor you see, especially if you’re hospitalized or see a specialist.
Monitor side effects. Mild dizziness or a gentle cough can be normal, but sudden swelling, severe fatigue, or chest pain need prompt medical attention. Know which signs mean “call the doctor now.”
Finally, schedule regular check‑ups. Blood tests, blood pressure readings, and heart imaging help your doctor fine‑tune the regimen. Adjustments are common, and that’s a good thing—your treatment should evolve with your health.
Managing cardiac medication feels like a team sport. You bring the questions; your doctor and pharmacist bring the expertise; the medication does the heavy lifting. Stick to the basics—take the right dose at the right time, watch for interactions, and keep the lines of communication open. With those habits in place, you give your heart the best chance to stay strong and steady.
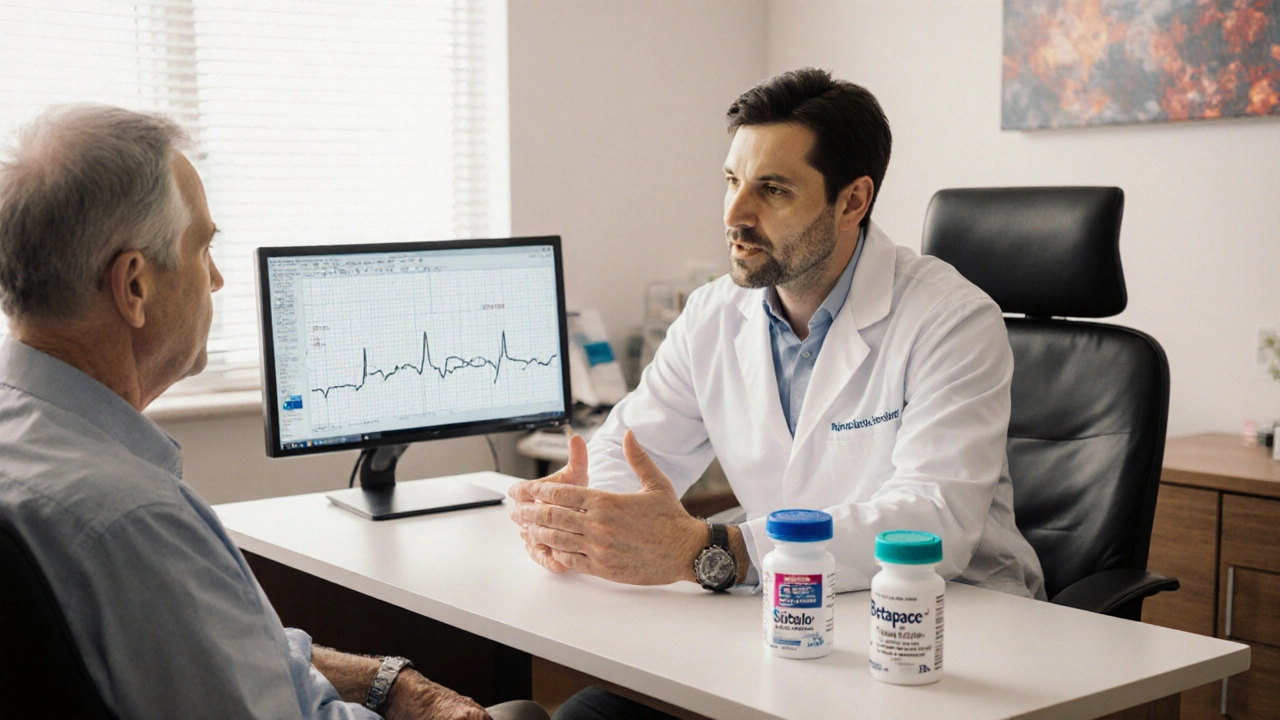

Compare Betapace (sotalol) with top anti‑arrhythmic alternatives, covering mechanisms, dosing, side effects, and when to choose each.

Seasonal affective disorder causes winter depression with fatigue, low mood, and cravings. Bright light therapy is a proven, drug-free treatment that resets your body clock and lifts mood in just days.

Warfarin and DOACs are both blood thinners used to prevent clots, but DOACs are now preferred for most patients due to better safety, fewer interactions, and no need for regular blood tests. Learn the key differences and what to do in an emergency.

The 180-day exclusivity rule under the Hatch-Waxman Act was meant to speed up generic drug entry-but now it often delays it. Learn how patent challenges, FDA rules, and corporate strategy keep prices high and patients waiting.

Authorized generics are the exact same drug as the brand-name version, made by the same company, but sold under a generic label. Learn how they work, why they exist, and how to spot them to save money without sacrificing quality.
When switching health plans, your generic drug coverage can save or cost you hundreds a year. Learn how formulary tiers, deductibles, and state rules impact your prescription costs-and how to avoid expensive surprises.