When working with personalized medicine, an approach that tailors treatment to a person’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health status. Also known as precision medicine, it strives to match the right drug, dose, and plan to each individual.
One of the core pillars of personalized medicine is pharmacogenomics, the study of how genes affect drug response. This field provides the scientific bridge between a patient’s DNA and the medicines they take. By decoding genetic variants, clinicians can predict which drugs will work best and which may cause adverse reactions.
To turn pharmacogenomic data into action, genetic testing, a lab analysis that reveals DNA variants influencing medication effectiveness is essential. Tests can be ordered before prescribing a new antidepressant, an anticoagulant, or a cancer therapy. The results often dictate whether a standard dose is safe or if an adjusted regimen is needed.
Personalized medicine encompasses pharmacogenomics, but it also relies on understanding drug interactions, how different medications affect each other's efficacy and safety. Even if a genetic test shows a patient should tolerate a certain drug, a concurrent medication could still raise toxicity risk. Clinicians use interaction checkers to spot these hidden hazards before finalizing a plan.
Another critical element is precision dosing, the practice of fine‑tuning drug amounts based on individual factors. Instead of the traditional “one dose fits all,” precision dosing adjusts numbers according to age, kidney function, and genetic markers. This approach reduces trial‑and‑error and speeds up symptom relief.
Semantic relationships become clear: pharmacogenomics informs drug selection, genetic testing guides dose adjustment, drug interactions influence the success of tailored therapy, and precision dosing refines the overall personalized medicine strategy. Together they form a feedback loop that continuously improves patient outcomes.
In everyday practice, doctors start with a patient’s medical history, run a genetic test if the medication carries known gene‑driven risks, and then check for possible drug interactions. The next step is to set an initial dose that reflects both the genetic insight and the patient’s organ function. Follow‑up labs confirm whether the chosen dose hits the therapeutic window or needs tweaking.
Real‑world examples illustrate the impact. For a patient with a CYP2C19 variant, clopidogrel may be less effective, prompting a switch to ticagrelor. For someone carrying the SLCO1B1*5 allele, simvastatin doses are lowered to avoid muscle damage. These decisions happen without guesswork because the underlying genetics are known.
Technology plays a big role, too. Electronic health records now embed pharmacogenomic alerts, so when a prescriber selects a drug, the system automatically flags a genetic contraindication or suggests an alternative. This integration turns data into action at the point of care.
Patients also benefit from education. Knowing why a specific drug was chosen helps adherence, and understanding potential interactions empowers them to report over‑the‑counter supplements that could interfere. Shared decision‑making becomes more meaningful when both sides speak the same scientific language.
While the promise of personalized medicine is huge, challenges remain. Not every drug has a validated genetic marker, insurance coverage for testing varies, and clinicians need training to interpret results correctly. Nonetheless, the field is moving fast, and new guidelines are emerging yearly.
Our curated collection below dives deeper into these topics. You’ll find practical diet tips that support hormone balance, insights on how specific drugs like mefenamic acid affect bone health, comparisons of immunosuppressants, and guides on buying affordable generics online. Each article ties back to the core ideas of personalized medicine, showing how genetics, drug interactions, and precise dosing shape real treatment choices.

Explore how genetics, therapeutic monitoring, and new delivery methods can personalize ethambutol therapy, reduce eye toxicity, and boost TB treatment success.

A clear, side‑by‑side comparison of Decadron (dexamethasone) and common steroid alternatives, covering potency, dosing, uses, side‑effects, and safety tips.
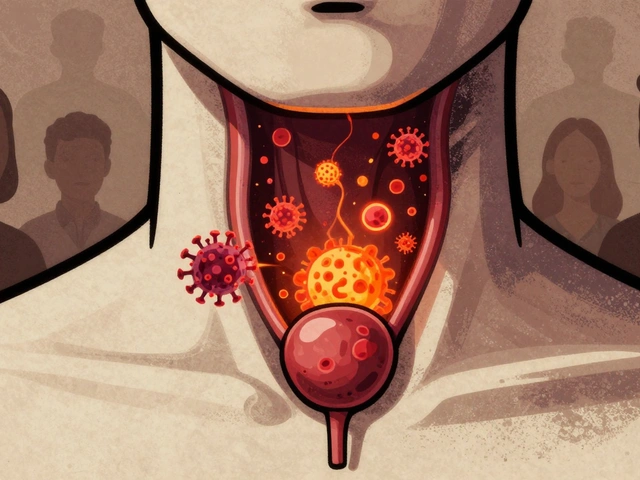
HPV causes thousands of throat and anal cancers each year in the U.S., with rising rates among men. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent these cancers - yet coverage remains too low. Learn how HPV leads to cancer and what you can do to stop it.
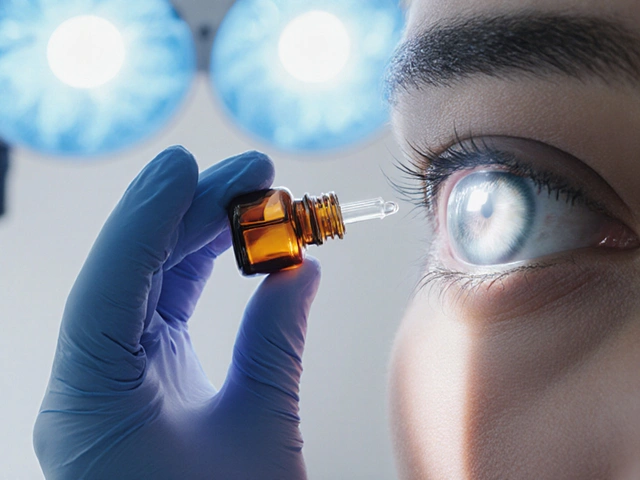
A side‑by‑side look at Cyclogyl (cyclopentolate) versus other mydriatic eye drops, covering onset, duration, safety, cost and best‑use scenarios.
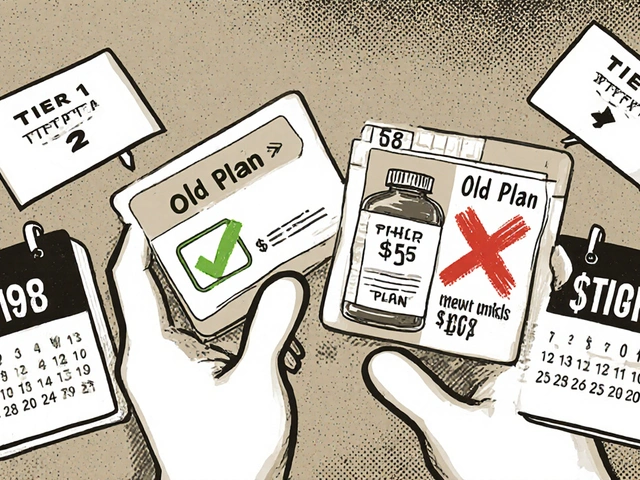
When switching health plans, your generic drug coverage can save or cost you hundreds a year. Learn how formulary tiers, deductibles, and state rules impact your prescription costs-and how to avoid expensive surprises.

Learn how progesterone affects gut motility, bile flow, and microbiome health, recognize deficiency signs, and discover natural and medical ways to improve digestion.