If you or a loved one has Parkinson's, the first question is usually "Which medicine works best?" The market is full of pills, patches, and gels, each with its own pros and cons. This page cuts through the noise and gives you a plain‑English rundown of the most common choices, so you can talk to your doctor with confidence.
Parkinson's symptoms vary from person to person. Some people need strong control of tremor, others fight stiffness or walking problems. Medications can differ in how fast they start working, how long the effect lasts, and what side effects they bring. Comparing them helps you avoid trial‑and‑error that can waste time and cause unnecessary discomfort.
Another reason to compare is cost. Some drugs have cheap generic versions, while others stay pricey because they’re brand‑only. Knowing the price range lets you budget and look for insurance coverage or discount programs early on.
Exelon (Rivastigmine) – This is a cholinesterase inhibitor approved for both Alzheimer's and Parkinson's‑related dementia. It comes as a capsule, oral solution, or skin patch. The patch is popular because it gives a steady dose all day and may cause fewer stomach issues. Expect an effect on memory and thinking within a few weeks, but it won’t stop tremor. Common side effects include nausea, loss of appetite, and mild dizziness.
Levodopa/Carbidopa – Often the first line for motor symptoms. Levodopa turns into dopamine in the brain, while carbidopa stops it from breaking down too early. It works fast, but long‑term use can lead to “off” periods where symptoms flare up. Adjusting timing and dosage with your doctor is key.
Pramipexole and Ropinirole – These are dopamine agonists that mimic dopamine’s action. They’re useful when levodopa isn’t enough or when you want to delay levodopa’s start. They may cause sleepiness, sudden urges to move (impulse control issues), or swelling in the ankles.
Selegiline – A MAO‑B inhibitor that blocks dopamine breakdown. It’s often added to levodopa for extra control. Common side effects are dry mouth and insomnia, especially at higher doses.
When you compare these options, ask yourself four simple questions: Does the drug target my main symptom? How quickly will I feel the benefit? What side effects am I willing to tolerate? And can I afford it?
Here’s a quick cheat‑sheet you can copy into a note:
Remember, every brain reacts a bit differently. What works for a neighbor might not work for you. Use this comparison as a starting point, then let your neurologist fine‑tune the plan.
Finally, keep a medication diary. Write down the dose, time, how you feel, and any side effects. Over a few weeks you’ll have solid data to discuss at your next appointment. A little record‑keeping can turn a frustrating guessing game into a clear conversation.
Parkinson's medication comparison doesn’t have to be a headache. With a basic knowledge of the main drugs, a simple checklist, and a habit of tracking your response, you’ll be better equipped to find the right balance between symptom control and quality of life.

A detailed comparison of Sinemet with other Parkinson's medications, covering benefits, drawbacks, costs, and when to switch for optimal symptom control.

Explore how liver failure impacts vision, from jaundice and dry eye to retinal hemorrhages, and learn practical steps to protect eye health while managing liver disease.

A clear comparison of Cleocin Gel (clindamycin) with other topical acne treatments, covering how they work, price, side effects, and tips for choosing the best option.
Cetirizine and levocetirizine both treat allergies, but levocetirizine causes less drowsiness. Learn why one might be better for daytime use and how to choose based on your needs.
Check your medicine cabinet twice a year to remove expired drugs and prevent accidents. Learn what to toss, where to store meds safely, and how to dispose of them the right way.
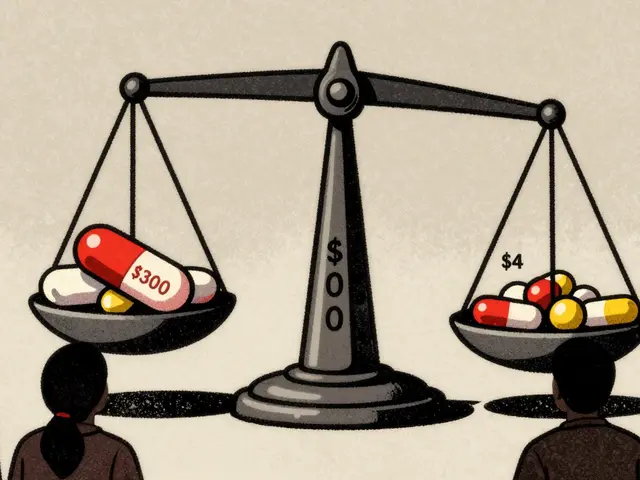

Buyers like Medicare use the presence of generic drugs to negotiate lower prices for brand-name medications. Generic competition drives prices down by over 90% in many cases, making it a key tool for controlling drug costs.